In the Blink of an Eye: Deciphering Blepharitis
Blepharitis refers to inflammation of the eyelids, typically at the edges where the eyelashes grow. It can affect one or both eyelids and often occurs bilaterally. The condition can be classified into anterior blepharitis, which affects the front of the eyelids, and posterior blepharitis, which affects the inner eyelid margin (meibomian glands).
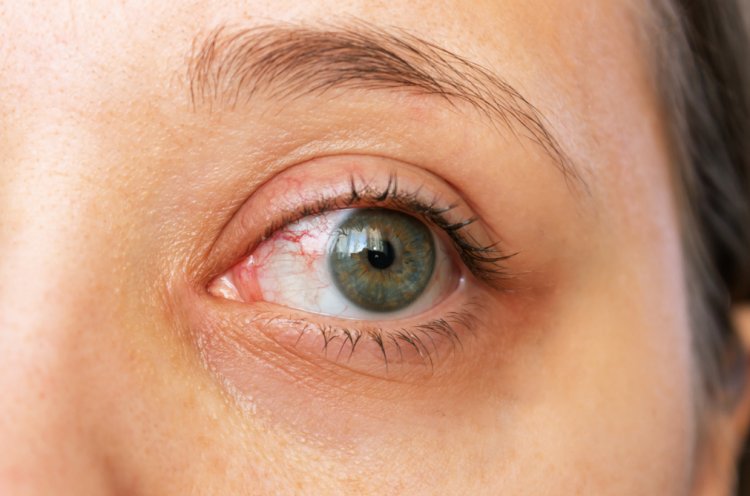
Causes of Blepharitis
Blepharitis can have various underlying causes, including:
- Bacterial infection (most commonly Staphylococcus aureus)
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Rosacea
- Allergies
- Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD)
- Demodex mites infestation
The exact cause may vary among individuals, and often, multiple factors contribute to the development of blepharitis.
Symptoms of Blepharitis
Common symptoms of blepharitis include:
- Redness and swelling of the eyelids
- Itchiness or irritation
- Burning or gritty sensation in the eyes
- Crusting or flakes at the base of the eyelashes
- Excessive tearing or dry eyes
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Blurred vision
Symptoms may fluctuate in severity and can be exacerbated by factors such as poor eyelid hygiene, stress, or environmental conditions.
Diagnosis of Blepharitis
Diagnosing blepharitis typically involves a comprehensive eye examination by an ophthalmologist or optometrist. The healthcare provider may:
- Examine the eyelids and eyelashes for signs of inflammation, crusting, or redness.
- Assess tear film quality and quantity.
- Check for meibomian gland dysfunction.
In some cases, additional tests such as a swab culture or eyelid biopsy may be conducted to identify the underlying cause, especially if infection is suspected.
Treatment Options for Blepharitis
Treatment for blepharitis aims to alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve eyelid hygiene. Common treatment options include:
- Warm compresses
- Lid hygiene
- Eyelid scrubs
- Antibiotics
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Lubricating eye drops
- Management of underlying conditions
Prognosis and Complications
With proper treatment and ongoing eyelid hygiene, most cases of blepharitis can be effectively managed. However, the condition may recur, requiring continued maintenance therapy. Without adequate management, blepharitis can lead to complications such as:
- Chronic dry eye syndrome
- Meibomian gland dysfunction
- Corneal complications
- Eyelash abnormalities
Regular follow-up with an eye care professional is essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
Blepharitis is a common eyelid condition characterized by inflammation and irritation. While it can be chronic and challenging to manage, proper eyelid hygiene and treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. If you experience symptoms of blepharitis, seek evaluation and guidance from an eye care specialist for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
#EyeHealth #EyelidCare #BlepharitisAwareness #EyeCareTips #HealthyEyes #EyeHygiene #VisionCare #EyeWellness #Optometry #Ophthalmology #EyeHealthMatters #BlepharitisTreatment #EyeComfort #EyeLove #EyeCareRoutine #EyeProblems #EyeSymptoms #EyeConditions #EyeCareAwareness #EyelidInflammation #EyeWellbeing #OptimalVision #EyeCareProfessional #EyeComfortZone
What's Your Reaction?





















