Achieve Radiant Skin: Proven Methods to Combat Hyperpigmentation
Skin spots, also known as hyperpigmentation, are common dermatological conditions characterized by patches of skin that appear darker than the surrounding areas. These spots can vary in size, shape, and color intensity, and they can occur for a variety of reasons, including sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, and aging. Understanding the underlying causes, different types of skin spots, and the available treatment options is essential for effectively managing and treating this condition.
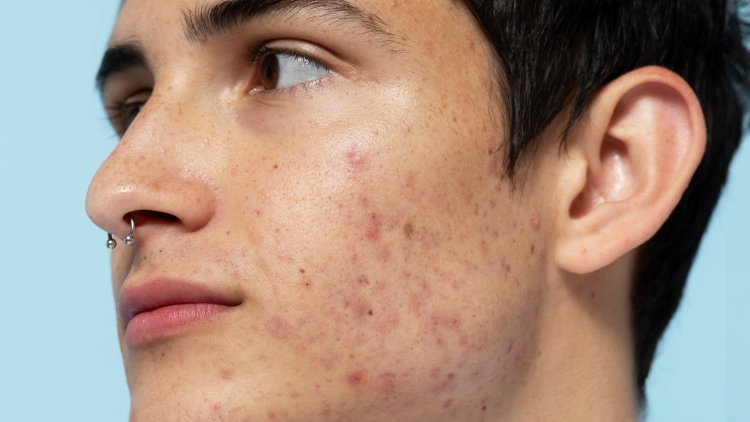
Causes of Skin Spots
Sun Exposure and Sunspots:
Sunspots, also known as solar lentigines or liver spots, are one of the most common types of skin spots. They develop as a result of prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. UV rays stimulate the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, leading to localized areas of darkened skin. Sunspots typically appear on sun-exposed areas such as the face, hands, arms, and shoulders.
Hormonal Changes and Melasma:
Melasma is another prevalent type of hyperpigmentation characterized by brown to gray-brown patches on the face. It is more common in women and often occurs during pregnancy (chloasma or "mask of pregnancy"), with the use of hormonal contraceptives, or during hormonal changes associated with menopause. Melasma occurs due to hormonal stimulation of melanocytes and is exacerbated by sun exposure.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH):
PIH refers to darkened spots or patches that develop after an inflammatory skin condition heals. Common causes include acne, eczema, psoriasis, and allergic reactions. Inflammation triggers an increase in melanin production, resulting in persistent pigmentation even after the initial condition has resolved. PIH can affect individuals with all skin types but is more noticeable in individuals with darker skin tones.
Age-related Hyperpigmentation:
Age spots, also known as solar lentigines or senile lentigo, are flat, brown, or grayish patches that typically appear on areas of the skin that have received the most sun exposure over the years. They are common in older adults and are caused by cumulative sun damage and the natural aging process, which leads to a decrease in skin cell turnover and repair mechanisms.
Types of Skin Spots
Sunspots (Solar Lentigines):
Sunspots are characterized by flat, tan, brown, or black spots that develop on sun-exposed areas of the skin. They are typically harmless but can increase in number and size with continued UV exposure. Sunspots are more prevalent in individuals with fair skin and tend to appear more frequently as people age.
Melasma:
Melasma presents as symmetric, blotchy patches of darker skin on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. It is triggered by hormonal changes and exacerbated by UV exposure. Melasma patches can vary in size and intensity and may fade somewhat during winter months or with strict sun protection, only to reappear or worsen with increased sun exposure.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH):
PIH manifests as darkened patches or spots that develop after an inflammatory skin condition has healed. These spots can range in color from pink, red, brown, or black, depending on the person's skin tone and the severity of the initial inflammation. PIH can persist for months or even years after the triggering inflammation has resolved.
Age Spots (Solar Lentigo or Senile Lentigo):
Age spots are small, flat, darkened patches of skin that typically appear on areas of the skin that have been exposed to sunlight over the years. They are more common in older adults and are characterized by their flat, oval shape and uniform coloration. Age spots are benign but can be cosmetically bothersome for some individuals.
Treatment Options for Skin Spots
Topical Treatments:
-
Hydroquinone: A common skin-lightening agent that inhibits melanin production. Available in over-the-counter formulations (2%) and prescription-strength (4%). Hydroquinone is typically used for short periods due to potential side effects such as skin irritation and hypo-pigmentation.
-
Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives that promote cell turnover and help fade dark spots over time. Retinoids are available in both prescription and over-the-counter formulations and are often used in combination with other skin-lightening agents for enhanced efficacy.
-
Kojic Acid: A natural skin-lightening agent derived from fungi that inhibits melanin production. Kojic acid is found in many skincare products, including creams, serums, and masks, and is suitable for all skin types.
Chemical Peels:
-
Glycolic Acid Peel: A type of alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) peel that exfoliates the skin's outer layer, promoting cell turnover and reducing the appearance of dark spots. Glycolic acid peels are available in various strengths and can be performed by dermatologists or licensed skincare professionals.
-
Salicylic Acid Peel: A beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) peel that penetrates deep into the pores, exfoliating the skin and improving its texture and tone. Salicylic acid peels are particularly effective for treating acne-related hyperpigmentation and can be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
Laser and Light Therapies:
-
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy: A non-invasive treatment that uses broad-spectrum light to target melanin in the skin. IPL therapy can effectively lighten dark spots and improve overall skin tone and texture with minimal downtime.
-
Fractional Laser Therapy: A more targeted laser treatment that delivers precise wavelengths of light to specific areas of pigmentation. Fractional laser therapy promotes collagen production and accelerates skin healing, resulting in smoother, more even-toned skin.
-
Q-Switched Laser: Specifically targets pigmented lesions with short, high-energy pulses. This treatment is effective for stubborn or deep-seated pigmentation, such as melasma or resistant sunspots.
Cosmetic Procedures:
-
Microdermabrasion: A minimally invasive procedure that exfoliates the skin using a diamond-tipped wand or fine crystals, improving skin texture and reducing the appearance of superficial pigmentation.
-
Microneedling: Stimulates collagen production and enhances the penetration of topical treatments, such as vitamin C or skin-lightening agents. Microneedling is effective for treating both post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and age-related dark spots.
Prevention and Maintenance
Sun Protection:
The most crucial aspect of preventing and minimizing skin spots is sun protection. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days. Reapply sunscreen every two hours when outdoors and wear protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses to shield the skin from harmful UV rays.
Gentle Skincare Routine:
Adopt a gentle skincare regimen that includes cleansing, moisturizing, and exfoliating with mild products suitable for your skin type. Avoid aggressive scrubbing or harsh chemical treatments that can exacerbate inflammation and lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits:
Eat a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals to support overall skin health. Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water each day and manage stress levels through relaxation techniques, exercise, and adequate sleep.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
Hashtags:
#SkinCare #Hyperpigmentation #SkinSpots #Dermatology #SkinHealth
What's Your Reaction?





















