The Omega-3 Revolution: Unveiling the Power of Fatty Acids in Combating Inflammation
When it comes to fighting inflammation, the spotlight often shines on pharmaceutical interventions and various dietary practices. Yet, nestled within the realm of natural remedies, Omega-3 fatty acids emerge as a powerful ally in this battle. These essential fats, which are not produced by the body and must be obtained through diet or supplements, have been the subject of extensive research due to their significant role in reducing inflammation and promoting overall health.

Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The Basics
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats that are crucial for human health. They are classified into three primary types:
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA): Found primarily in plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA): Found mainly in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines.
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): Also predominantly found in fatty fish and important for brain health and visual function.
These fats are integral to various bodily functions and have been linked to reduced risks of chronic diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and inflammatory disorders.
The Inflammation Connection
Inflammation is a natural and essential response by the body’s immune system to injury or infection. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to various health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. Chronic inflammation is often the result of a poor diet, high levels of stress, and environmental toxins, and it can create a cycle of discomfort and disease.
How Omega-3s Influence Inflammation
Omega-3 fatty acids play a critical role in modulating the inflammatory response. Here's how they make a difference:
- Reducing Pro-inflammatory Eicosanoids: Inflammation is driven in part by eicosanoids, which are signaling molecules that promote inflammation. Omega-3s, particularly EPA and DHA, can compete with omega-6 fatty acids (which promote inflammation) for the same enzyme systems. This competition reduces the production of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids, thereby decreasing inflammation.
- Modulating Cytokine Production: Cytokines are proteins that facilitate communication between cells and play a role in the inflammatory process. Omega-3s help to regulate the production of cytokines, including reducing levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha and interleukin-6.
- Influencing Cell Membrane Composition: Omega-3s incorporate into cell membranes, altering their fluidity and function. This incorporation can lead to a more balanced production of inflammatory mediators and improve cellular responses to inflammatory stimuli.
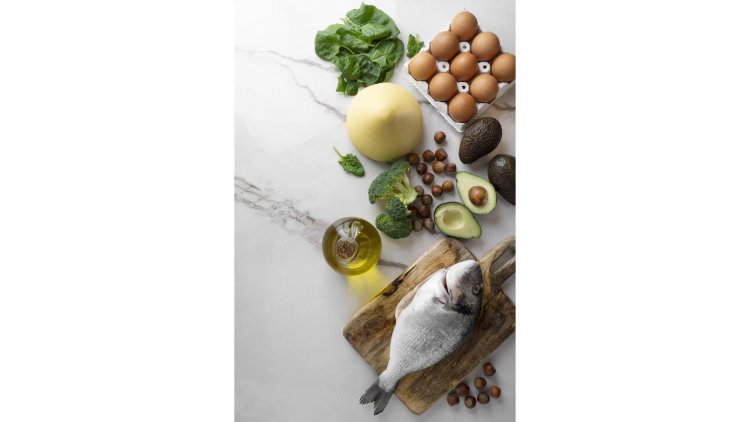

Dietary Sources of Omega-3s
To harness the anti-inflammatory benefits of Omega-3s, incorporating them into your diet is crucial. Here’s a look at some rich sources:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies are excellent sources of EPA and DHA. Aim for at least two servings of fatty fish per week to ensure adequate intake.
- Chia Seeds: A plant-based source rich in ALA, chia seeds can be added to smoothies, yogurt, or baked goods.
- Flaxseeds: Flaxseeds and flaxseed oil are another good source of ALA. Ground flaxseeds can be sprinkled on cereals, salads, or used in baking.
- Walnuts: Walnuts are a tasty way to include ALA in your diet. Enjoy them as a snack or add them to salads and other dishes.
- Algal Oil: For those who prefer not to consume fish, algal oil supplements provide a plant-based source of DHA.
Supplements: When and How to Use Them
For individuals who have difficulty obtaining sufficient Omega-3s from their diet, supplements can be an effective alternative. Fish oil capsules, algae-based supplements, and Omega-3-rich oils are popular options. However, it’s essential to choose high-quality supplements that are free from contaminants such as heavy metals and PCBs.
When considering Omega-3 supplements, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking other medications. They can help determine the appropriate dosage and form based on your specific needs.
The Balance Between Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids
While Omega-3s are vital for reducing inflammation, it's equally important to manage your intake of Omega-6 fatty acids. Omega-6s, found in many processed and fried foods, can promote inflammation when consumed in excess. Achieving a healthy balance between Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids is crucial for maintaining optimal health and managing inflammation effectively.
Integrating Omega-3s into a Balanced Diet
To maximize the anti-inflammatory benefits of Omega-3s, integrating them into a balanced and nutrient-rich diet is essential. Here are some practical tips for doing so:
- Plan Your Meals: Incorporate fatty fish into your weekly meal plan. Consider dishes like grilled salmon, sardine salads, or mackerel pâté. Aim to include other sources of Omega-3s such as chia seeds or flaxseed oil in your daily routine.
- Choose Whole Foods: Opt for whole, unprocessed foods that are naturally rich in Omega-3s and other nutrients. Whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins can support overall health and work synergistically with Omega-3s to reduce inflammation.
- Read Labels: When selecting packaged foods or supplements, check the labels for Omega-3 content and the ratio of Omega-3 to Omega-6 fatty acids. Avoid products high in Omega-6, which can counteract the benefits of Omega-3s.
- Cook with Omega-3-Rich Oils: Use oils like flaxseed oil or algae oil in salad dressings and cooking. However, avoid heating Omega-3 oils at high temperatures, as this can degrade their beneficial properties.
- Snack Wisely: Choose snacks that incorporate Omega-3 sources. Nuts and seeds, such as walnuts and chia seed pudding, can be satisfying and nutritionally beneficial alternatives to processed snack foods.
Omega-3s and Lifestyle Factors
While Omega-3s play a pivotal role in managing inflammation, they are most effective when combined with other healthy lifestyle practices. Here are some ways to enhance their benefits:
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can help modulate inflammatory responses in the body. Aim for regular, moderate exercise to complement the anti-inflammatory effects of Omega-3s.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can exacerbate inflammation. Incorporate stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises into your routine.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess body weight is associated with increased inflammation. A balanced diet, including Omega-3s, along with regular exercise, can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce inflammation.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for overall health and can influence inflammatory processes. Aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep per night.
- Limit Alcohol and Avoid Smoking: Both alcohol and smoking can contribute to inflammation and overall health deterioration. Reducing or eliminating these factors can enhance the benefits of Omega-3s.
The Future of Omega-3 Research
As research on Omega-3s continues to evolve, new insights and applications are emerging. Current studies are exploring:
- Personalized Nutrition: Investigating how genetic factors influence individual responses to Omega-3 supplementation and dietary intake, aiming to personalize recommendations for optimal health outcomes.
- Chronic Disease Management: Further exploring the role of Omega-3s in managing chronic diseases such as autoimmune disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer.
- Mental Health: Delving deeper into the impact of Omega-3s on mental health conditions beyond depression, including anxiety, bipolar disorder, and cognitive decline.
- Omega-3s and Gut Health: Examining how Omega-3s influence gut microbiota and gut health, potentially linking them to improved immune function and reduced inflammation.
Overall Summary
Omega-3 fatty acids represent a potent tool in the fight against inflammation. Their ability to modulate inflammatory pathways, influence cytokine production, and compete with pro-inflammatory eicosanoids underscores their importance in maintaining health and preventing chronic diseases. By incorporating Omega-3s through dietary sources or supplements and balancing them with a healthy lifestyle, individuals can significantly enhance their well-being and reduce inflammation.
As our understanding of Omega-3s grows, continued research will likely reveal even more benefits and applications for these remarkable fatty acids. For now, embracing a diet rich in Omega-3s and adopting complementary healthy practices can be a proactive approach to managing inflammation and promoting overall health.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
What's Your Reaction?