Xerostomia: An In-Depth Analysis
Xerostomia, often referred to as dry mouth, is a condition characterized by a decrease in saliva production, leading to dryness in the mouth. This condition is not a disease itself but rather a symptom indicative of various underlying health issues or side effects of certain treatments. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health, aiding digestion, and providing comfort. Reduced saliva production can significantly affect an individual's quality of life and lead to several health complications.
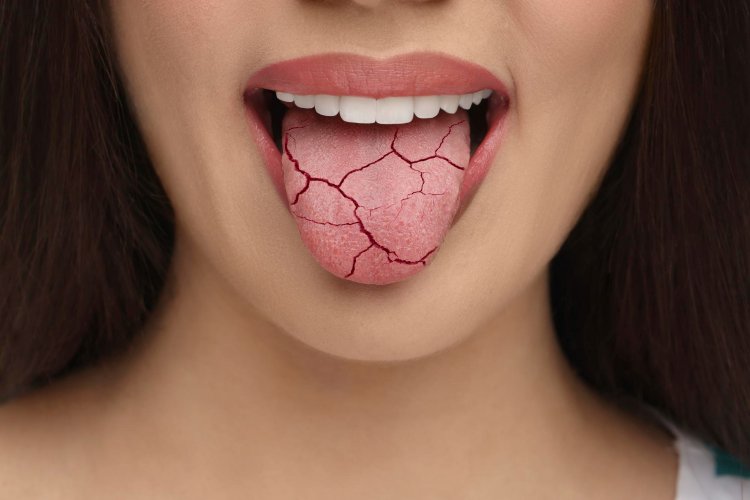
Causes of Xerostomia
Xerostomia can result from a variety of factors, including:
Medications
Over 400 medications list dry mouth as a side effect. These include:
- Antihistamines: Used for allergies.
- Decongestants: Common in cold and flu medications.
- Analgesics: Pain relievers.
- Diuretics: Often prescribed for hypertension.
- Antidepressants and Antianxiety medications: Used for mental health conditions.
- Muscle relaxants: For muscle spasms.
- Chemotherapy agents: Used in cancer treatment.
Aging
As people age, the salivary glands may not function as effectively, and the prevalence of medication use increases, both of which can contribute to dry mouth.
Medical Conditions
Several systemic diseases are associated with xerostomia, including:
- Sjögren's Syndrome: An autoimmune disease that targets salivary glands.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can reduce saliva production.
- HIV/AIDS: Can lead to salivary gland disease.
- Parkinson's Disease: A neurological disorder that can affect saliva production.
- Radiation Therapy: Treatment for head and neck cancers often involves radiation that can damage salivary glands, resulting in decreased saliva production.
Lifestyle Factors
Habits such as smoking, chewing tobacco, and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to dry mouth. Caffeine, found in coffee, tea, and many soft drinks, can also have a drying effect.
Nerve Damage
Injury or surgery that causes nerve damage in the head or neck can impair the function of salivary glands.
Symptoms of Xerostomia
The symptoms of xerostomia can vary in severity and may include:
- A persistent feeling of dryness or stickiness in the mouth.
- Frequent thirst.
- Sore throat or hoarseness.
- Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or speaking.
- A burning or tingling sensation in the mouth and on the tongue.
- Cracked lips or corners of the mouth.
- A dry, rough tongue.
- Mouth sores or oral infections, such as thrush (candidiasis).
Complications of Xerostomia
If left untreated, xerostomia can lead to several complications, including:
- Dental Decay: Saliva helps to wash away food particles and neutralize acids produced by bacteria in the mouth. A lack of saliva increases the risk of tooth decay.
- Gum Disease: Reduced saliva can contribute to the development of gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Mouth Infections: A dry environment is more susceptible to fungal infections like oral thrush.
- Difficulty Wearing Dentures: Saliva helps to create suction and a good fit for dentures; without it, dentures can become uncomfortable.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Difficulty in chewing and swallowing can lead to a poor diet and subsequent nutritional deficiencies.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing xerostomia involves a comprehensive approach that may include:
- Medical History Review: Assessment of medications and medical conditions that could contribute to dry mouth.
- Physical Examination: Examination of the mouth and salivary glands.
- Salivary Flow Test (Sialometry): Measuring the rate of saliva production.
- Blood Tests: To identify underlying diseases such as Sjögren's syndrome or diabetes.
- Imaging Studies: Such as sialography (an imaging technique to view salivary glands) or ultrasound.
Treatment and Management
While there is no definitive cure for xerostomia, various strategies can help manage and alleviate its symptoms:
Hydration
Drinking water regularly and using a humidifier can help keep the mouth moist.
Saliva Substitutes and Stimulants
Over-the-counter saliva substitutes can provide temporary relief. Medications like pilocarpine and cevimeline can stimulate saliva production in some cases.
Oral Hygiene
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is crucial. This includes brushing with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using antimicrobial mouth rinses to prevent infections.
Dietary Adjustments
Avoiding sugary, acidic, and caffeinated foods and drinks can help reduce the risk of dental decay and discomfort.
Lifestyle Modifications
Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake are beneficial. Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free candies can also stimulate saliva flow.
Regular Dental Visits
Frequent check-ups with a dentist are essential to monitor oral health and address issues promptly.
Conclusion
Xerostomia is a common condition that can significantly impact a person's oral health and overall quality of life. Understanding the various causes, symptoms, and management strategies is essential for effectively addressing this condition. With appropriate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans, individuals suffering from xerostomia can achieve better oral comfort and health outcomes. Continuous research and awareness are necessary to improve the management and treatment of this condition, ultimately enhancing patient quality of life.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
Hashtags
#Xerostomia #DryMouth #OralHealth #HealthTips #MedicalAdvice #DentalCare #HealthyLifestyle
What's Your Reaction?





















