Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are one of the most common infections affecting millions of individuals worldwide each year. These infections can occur in any part of the urinary tract, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. UTIs can be uncomfortable and sometimes painful, but they are usually easily treatable with medications.
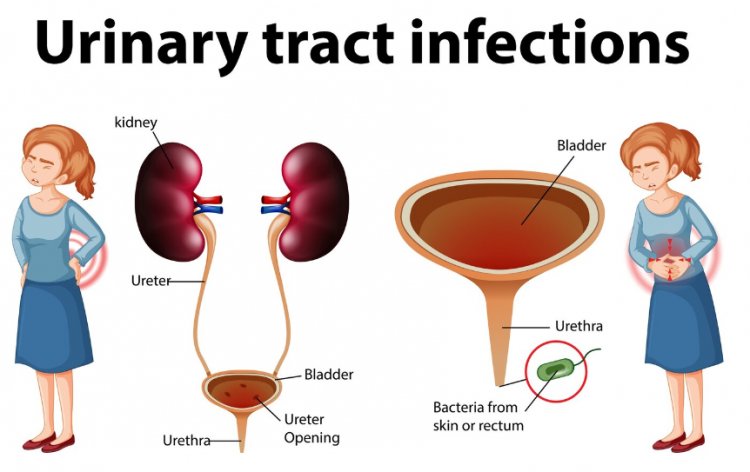
Causes of UTIs:
UTIs typically occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder. The most common bacteria associated with UTIs is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is normally found in the digestive tract. Other bacteria such as Klebsiella and Proteus can also cause UTIs.
Several factors can increase the risk of developing a UTI, including:
- Gender: Women are more prone to UTIs than men, mainly due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily.
- Sexual activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, increasing the risk of infection.
- Urinary tract abnormalities: Conditions such as kidney stones or urinary retention can obstruct the flow of urine, making it easier for bacteria to multiply.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV/AIDS, are at higher risk of developing UTIs.
- Urinary catheter use: Catheters can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, leading to infection, especially if left in place for an extended period.
Symptoms of UTIs:
The symptoms of a UTI can vary depending on which part of the urinary tract is affected. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Frequent urination
- Strong, persistent urge to urinate
- Cloudy or bloody urine
- Pelvic pain in women
- Rectal pain in men
- Fever and chills (if the infection spreads to the kidneys)
It's essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, as untreated UTIs can lead to more severe complications, such as kidney infections or sepsis.
Treatment of UTIs:
The primary treatment for UTIs involves antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. The type of antibiotic prescribed will depend on the severity of the infection and the specific bacteria involved. Commonly prescribed antibiotics for UTIs include trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, and ciprofloxacin.
In addition to antibiotics, individuals with UTIs are encouraged to drink plenty of water to help flush out the bacteria from the urinary tract. Avoiding irritants such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods can also help alleviate symptoms.
In some cases, particularly for recurrent UTIs, healthcare providers may recommend additional measures such as low-dose antibiotics taken over an extended period or vaginal estrogen therapy for postmenopausal women to reduce the risk of recurrent infections.
Prevention of UTIs:
While UTIs are common, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing an infection:
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Practice good hygiene: Wiping from front to back after using the toilet can help prevent the spread of bacteria from the anus to the urethra.
- Urinate after sex: Emptying the bladder after sexual intercourse can help flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urinary tract.
- Avoid irritating products: Using gentle, unscented hygiene products and avoiding the use of douches and sprays in the genital area can help prevent irritation that could lead to UTIs.
In conclusion, UTIs are common infections of the urinary tract that can cause discomfort and pain if left untreated. However, with prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment, most UTIs can be easily resolved. By taking preventive measures and practicing good hygiene, individuals can reduce their risk of developing UTIs and maintain urinary tract health.
Clinics in the United Kingdom:
- London Urology Associates - London
- The Birmingham Prostate Clinic - Birmingham
- The Urology Hospital London - London
- The Urology Foundation - London
- The Bristol Urology Clinic - Bristol
Clinics in Turkey:
- Memorial Ankara Hospital Urology Clinic - Ankara
- Liv Hospital Ulus Urology Clinic - Istanbul
- Acıbadem Maslak Hospital Urology Clinic - Istanbul
- Florence Nightingale Istanbul Urology Clinic - Istanbul
- Anadolu Medical Center Urology Clinic - Istanbul
Discover Coupoly's exclusive Medical Concierge Service, connecting you with renowned doctors and clinics, alongside our complimentary Travel Concierge Service, linking you with top UK travel agencies.
Contact us now to learn more.
Get in Touch
What's Your Reaction?





















