Unraveling the Complexity of Brain Activity: An In-Depth Exploration of Electroencephalography (EEG)
The human brain, with its intricate network of billions of neurons firing in orchestrated patterns, remains one of the most fascinating frontiers in science. Amidst this complexity, Electroencephalography (EEG) emerges as a powerful tool, offering unparalleled insights into the inner workings of the brain. In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to unravel the multifaceted world of EEG, exploring its principles, applications, and significance in neuroscience and clinical practice.
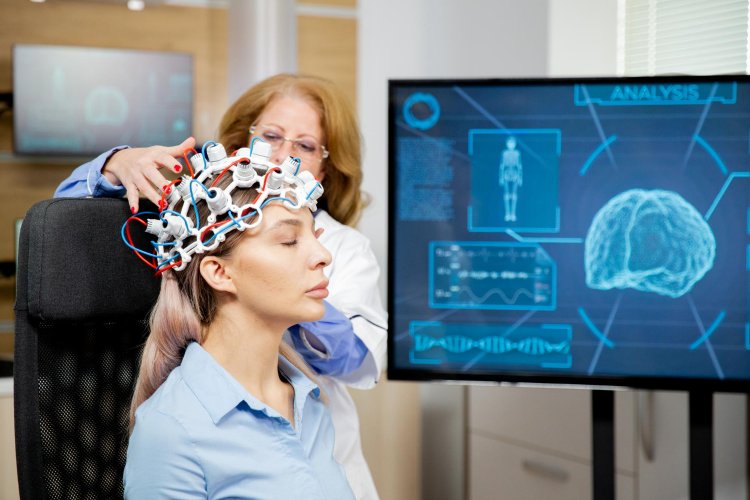
Understanding EEG:
At its essence, EEG is a non-invasive neurophysiological technique that measures the electrical activity generated by the firing of neurons in the brain. This electrical activity, manifested as rhythmic oscillations known as brainwaves, provides a window into various cognitive processes and neurological conditions. By capturing and analyzing these brainwaves, EEG enables researchers and clinicians to decipher the intricate language of the brain, offering invaluable insights into its function and dysfunction.
The Process of EEG Recording:
The process of EEG recording begins with meticulous preparation, ensuring that the scalp is clean and free of any substances that may interfere with electrode conductivity. Electrodes, strategically placed according to standardized systems such as the 10-20 system, are then affixed to specific locations on the scalp. Conductive gel or paste is applied to these electrodes to optimize electrical contact, facilitating the accurate capture of brainwave activity. Once the electrodes are in place, the EEG recording commences, with the patient instructed to remain still and relaxed. The recorded signals are amplified, filtered, and displayed as waveforms on a computer screen, providing a visual representation of brain activity for further analysis.
Applications of EEG:
-
Diagnostic Tool in Neurology: EEG serves as a cornerstone in the diagnosis and management of various neurological disorders, including epilepsy, sleep disorders, and brain tumors. By detecting abnormal patterns of brain activity, EEG aids clinicians in formulating precise diagnoses and guiding treatment strategies, thereby improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
-
Monitoring Brain Function: In critical care settings such as intensive care units (ICUs) and operating rooms, EEG plays a pivotal role in monitoring brain function. Continuous EEG monitoring allows for the early detection of cerebral ischemia, seizure activity, and other neurological complications, enabling prompt intervention to mitigate potential harm and optimize patient outcomes.
-
Assessment of Cognitive Function: EEG serves as a valuable tool for assessing cognitive function across diverse populations. By examining neural oscillations associated with cognitive processes such as attention, memory, and executive function, EEG provides insights into cognitive performance and the effects of aging, disease, and interventions on cognitive function. From evaluating cognitive decline in neurodegenerative disorders to assessing cognitive enhancement strategies, EEG offers a window into the complexities of the human mind.
-
Research in Neuroscience: EEG is instrumental in advancing our understanding of brain function and dysfunction. Its high temporal resolution allows researchers to investigate neural dynamics underlying sensory processing, motor control, language comprehension, and emotional regulation, among other cognitive processes. Through sophisticated analyses of EEG data, researchers unravel the intricacies of the brain, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries and innovative therapies in neuroscience.
-
Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) Development: EEG-based BCIs represent a cutting-edge application of EEG technology, enabling direct communication between the brain and external devices. By decoding neural signals associated with specific intentions or commands, EEG-based BCIs empower individuals with severe motor disabilities to control assistive devices, interact with computers, and communicate with others, thereby enhancing their autonomy and quality of life. From restoring mobility to enabling communication, EEG-based BCIs hold immense promise for revolutionizing the lives of individuals with disabilities.
In conclusion, Electroencephalography (EEG) stands as a versatile and indispensable tool in neuroscience and clinical medicine. From unraveling the mysteries of the brain to diagnosing neurological disorders, monitoring critical patients, assessing cognitive function, and driving innovation in brain-computer interfaces, EEG continues to revolutionize our understanding of the human brain and improve patient care. As technology advances and our understanding of brain function deepens, EEG will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of neuroscience research and clinical practice, guiding us on our quest to unlock the secrets of the mind.
#UnderstandingEEG #EEGRecording #Neurology #BrainFunction #CognitiveFunction #NeuroscienceResearch #BCI #BrainHealth #HealthcareTech
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
What's Your Reaction?





















