Knee Fluid Loss: Symptoms, Causes, Natural Treatment Methods
Knee fluid loss, also known as knee joint effusion or synovial fluid deficiency, refers to a condition where there is a reduction in the quantity or quality of synovial fluid within the knee joint. This fluid plays a crucial role in lubricating the joint, cushioning it against impact, and facilitating smooth movement.
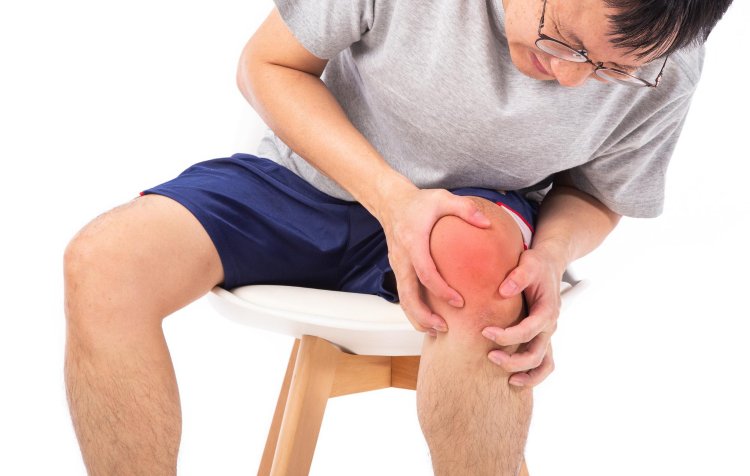
Symptoms of Knee Fluid Loss:
Pain
Individuals may experience increased pain, particularly with activities that stress the knee joint such as walking, climbing stairs, or bending.
Swelling
Visible swelling around the knee joint is a common symptom of fluid accumulation. The knee may appear enlarged and feel warm to the touch.
Stiffness
Limited flexibility in the knee joint, making it difficult to fully bend or straighten the leg.
Instability
A sensation of the knee giving way or feeling unstable, which can impact balance and mobility.
Reduction in Range of Motion
Difficulty in moving the knee through its full range of motion, affecting activities of daily living and physical performance.
Causes of Knee Fluid Loss:
Injury
Traumatic events such as sports injuries, falls, or accidents can lead to acute knee effusion. This may involve damage to ligaments, menisci, or fractures affecting the joint.
Arthritis
Chronic inflammatory conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can cause persistent inflammation within the joint, resulting in synovial fluid depletion over time.
Overuse
Repetitive stress on the knee joint from activities such as running, jumping, or kneeling can lead to inflammation and fluid buildup.
Infection
Septic arthritis, a bacterial infection of the joint, can cause rapid onset of knee effusion and significant joint damage if not promptly treated.
Metabolic Conditions
Obesity, which places excessive stress on weight-bearing joints, and certain metabolic disorders can also contribute to knee joint fluid loss.
Natural Treatment Methods for Knee Fluid Loss:
Rest and Ice
Resting the knee and applying ice packs can help alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
Compression
Using an elastic bandage or knee sleeve provides support, reduces swelling, and improves joint stability.
Elevation
Keeping the affected knee elevated above heart level can aid in reducing swelling by promoting fluid drainage.
Physical Therapy
Gentle exercises prescribed by a physical therapist can help strengthen muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and prevent stiffness.
Nutrition and Hydration
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids supports joint health. Drinking plenty of water ensures proper hydration, which is essential for synovial fluid production.
Supplements
Some individuals may benefit from supplements like glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, or turmeric (curcumin) for their anti-inflammatory and joint-supporting properties.
Why Knee Fluid Loss Occurs in Younger Individuals
In younger individuals, knee fluid loss often stems from sports-related injuries, overuse during physical activities, or congenital abnormalities affecting joint structure and function. Preventive measures such as proper warm-up exercises, using protective gear, and adopting sound biomechanical practices are crucial in reducing the risk of knee joint injuries.
In conclusion, knee fluid loss can significantly impair joint function and quality of life if left untreated. Understanding the symptoms, underlying causes, and effective natural treatment options empowers individuals to manage their condition proactively. Seeking timely medical evaluation and guidance from healthcare professionals ensures appropriate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
By adopting a comprehensive approach to joint health, incorporating appropriate lifestyle modifications, and utilizing effective treatment strategies, individuals can minimize symptoms, improve knee function, and enhance overall well-being.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
#KneeHealth #JointCare #NaturalTreatment #InjuryRecovery #Arthritis #PhysicalTherapy #HealthyLiving #Wellness #Fitness #PainRelief #Healthcare
What's Your Reaction?





















