Seborrheic Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
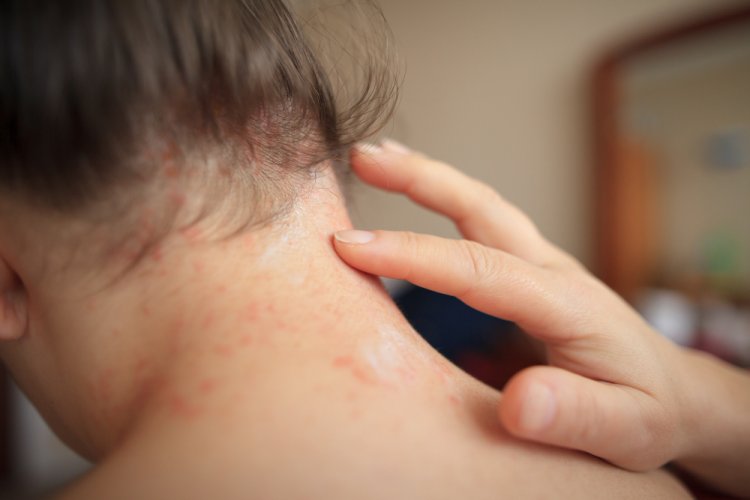
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that mainly affects the scalp, but it can also occur in other oily areas of the body such as the face, chest, and back. It is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by red, itchy, and flaky skin. While the exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is not fully understood, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors.
Causes of Seborrheic Dermatitis:
Malassezia Yeast:
Malassezia is a type of yeast that normally lives on the skin's surface without causing any problems. However, in individuals with seborrheic dermatitis, this yeast may proliferate excessively, leading to inflammation and skin symptoms.
Sebaceous Glands:
Seborrheic dermatitis tends to occur in areas with a high density of sebaceous (oil-producing) glands. Excessive production of sebum, the skin's natural oil, may contribute to the development of the condition.
Hormonal Factors:
Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during puberty or in individuals with certain medical conditions like Parkinson's disease or HIV/AIDS, may increase the risk of developing seborrheic dermatitis.
Environmental Triggers:
Cold, dry weather conditions or exposure to harsh chemicals can exacerbate symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis.
Genetic Predisposition:
There is evidence to suggest that a genetic predisposition may play a role in the development of seborrheic dermatitis, as it often runs in families.
Symptoms of Seborrheic Dermatitis:
-
Flaky, Greasy Skin: The most common symptom of seborrheic dermatitis is the presence of yellow or white flakes (dandruff) on the scalp, eyebrows, beard, or other affected areas.
-
Redness and Inflammation: The skin may appear red and inflamed, and in severe cases, it may become swollen and tender to the touch.
-
Itching and Discomfort: Seborrheic dermatitis can cause intense itching, which may worsen with scratching and lead to further irritation.
-
Oily or Dry Skin: Depending on the individual, seborrheic dermatitis can manifest as either oily or dry skin. Some areas may be greasy and oily, while others may be dry and flaky.
Treatment of Seborrheic Dermatitis:
-
Medicated Shampoos: Over-the-counter shampoos containing ingredients such as ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or coal tar can help reduce inflammation and control yeast growth on the scalp.
-
Topical Steroids: In cases of severe inflammation, topical corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce redness, itching, and swelling.
-
Antifungal Creams: Antifungal creams or lotions containing ingredients like clotrimazole or ciclopirox can help inhibit the growth of Malassezia yeast on the skin.
-
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: Drugs like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus may be recommended for individuals who do not respond to traditional treatments or have concerns about long-term steroid use.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding harsh soaps, minimizing stress, and maintaining good hygiene practices can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
In conclusion, seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition characterized by redness, itching, and flaking of the skin. While it cannot be cured, it can be effectively managed with a combination of medicated shampoos, topical treatments, and lifestyle modifications. If you suspect you have seborrheic dermatitis, it is important to consult a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
#SeborrheicDermatitis #SkinCare #Dermatology #HealthySkin #SkinHealth #FlakySkin #ItchySkin #SkinConditions #Dandruff #ScalpCare #SkinInflammation #NaturalRemedies #SkinTreatment #HealthyLiving #Wellness #SelfCare
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
What's Your Reaction?





















