Laparoscopy: A Comprehensive Overview of Minimally Invasive Surgery
Laparoscopy, a cornerstone of modern surgery, has redefined the way many surgical procedures are performed. From its humble beginnings in the early 20th century to its current status as a gold standard in many surgical specialties, laparoscopy has undergone significant advancements, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced morbidity. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the history, techniques, applications, advantages, limitations, and future prospects of laparoscopic surgery.
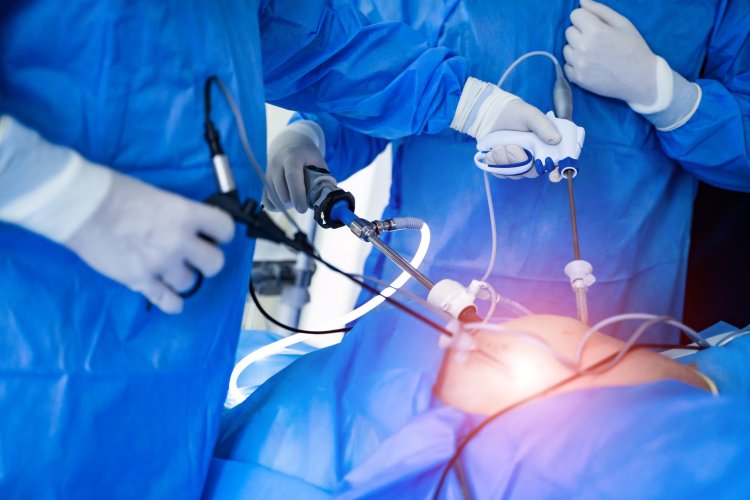
History
The roots of laparoscopy can be traced back to the pioneering work of Dr. Georg Kelling, a German surgeon who performed the first laparoscopic procedures on dogs in 1901. However, it was not until the 1980s that laparoscopy gained widespread acceptance in human surgery. Dr. Kurt Semm, a German gynecologist, is credited with performing the first laparoscopic appendectomy in 1980, marking a significant milestone in the history of surgery. Since then, laparoscopy has evolved rapidly, driven by advancements in technology, instrumentation, and surgical techniques.
Techniques
Laparoscopic surgery involves the use of small incisions (typically less than 1 centimeter in length) through which specialized instruments and a camera called a laparoscope are inserted into the abdominal cavity. The laparoscope, equipped with a high-definition camera, provides real-time images of the internal organs on a monitor, allowing the surgeon to visualize the surgical field with exceptional clarity. Carbon dioxide gas is used to inflate the abdomen, creating a workspace and facilitating better visualization and instrument manipulation. Various surgical procedures, including but not limited to cholecystectomy, appendectomy, hernia repair, hysterectomy, and prostatectomy, can be performed using laparoscopic techniques.
Applications
Laparoscopy has found widespread applications across multiple surgical specialties, including general surgery, gynecology, urology, and bariatric surgery. In general surgery, laparoscopy is commonly used for procedures such as cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal), appendectomy, and colorectal surgery. In gynecology, laparoscopic techniques are employed for hysterectomy, ovarian cystectomy, myomectomy, and tubal ligation. Urological procedures such as nephrectomy, prostatectomy, and cystectomy can also be performed laparoscopically, offering patients less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. Additionally, laparoscopic bariatric surgery has emerged as an effective treatment for obesity, with procedures like gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy yielding excellent long-term weight loss outcomes.
Advantages
Laparoscopy offers numerous advantages over traditional open surgery, both for patients and surgeons. One of the primary benefits is reduced postoperative pain, as smaller incisions result in less tissue trauma and nerve damage. Patients undergoing laparoscopic procedures typically experience shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times, allowing them to return to their normal activities sooner. The cosmetic outcome is also superior, with smaller scars and minimal wound complications. From a surgical standpoint, laparoscopy provides magnified, high-definition views of the surgical field, enabling surgeons to perform intricate maneuvers with greater precision and accuracy. Moreover, the minimally invasive nature of laparoscopy reduces the risk of complications such as infection, bleeding, and incisional hernias, leading to improved overall patient safety and satisfaction.
Limitations
Despite its numerous advantages, laparoscopy is not without limitations. One of the main challenges is the steep learning curve associated with mastering laparoscopic techniques. Surgeons require specialized training and considerable experience to perform laparoscopic procedures proficiently, particularly complex interventions. Additionally, certain surgical scenarios, such as extensive adhesions or large tumors, may pose technical challenges in laparoscopy and require conversion to open surgery. Furthermore, laparoscopic procedures can be more time-consuming compared to their open counterparts, particularly in the initial stages of a surgeon's learning curve. Cost considerations, including equipment expenses and longer operative times, may also limit the widespread adoption of laparoscopy in some healthcare settings.
Future Prospects
The future of laparoscopy holds promise, driven by ongoing technological innovations and advancements in surgical techniques. Robotic-assisted laparoscopy, which combines the precision of robotic systems with the dexterity of laparoscopic instruments, is increasingly being utilized in various surgical specialties. Robotic platforms offer advantages such as improved ergonomics, enhanced three-dimensional visualization, and wrist-like instrument articulation, making them particularly well-suited for complex procedures. Furthermore, advancements in imaging modalities, including fluorescence-guided surgery and augmented reality, have the potential to further enhance the capabilities of laparoscopic surgery by providing real-time intraoperative guidance and tissue characterization. Miniaturization of instruments, development of disposable robotic platforms, and integration of artificial intelligence algorithms are other areas of active research aimed at advancing the field of laparoscopy and expanding its applications.
In conclusion, laparoscopy has emerged as a cornerstone of modern surgical practice, offering patients safer, less invasive treatment options and surgeons enhanced visualization and precision. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a standard of care in many surgical specialties, laparoscopy has undergone remarkable evolution, driven by technological innovation and clinical experience. While challenges such as the learning curve and technical limitations persist, ongoing research and development efforts continue to push the boundaries of laparoscopic surgery, paving the way for a future where minimally invasive approaches become the norm rather than the exception. As we look ahead, the potential of laparoscopy to further improve patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and advance the field of surgery remains immense, reaffirming its status as one of the most transformative innovations in the history of medicine.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
Hashtags:
#Laparoscopy #Surgery #MinimallyInvasive #MedicalAdvancements #Healthcare #SurgicalTechniques #RoboticSurgery #FutureOfMedicine
What's Your Reaction?





















