Gum Diseases and Systemic Health: Exploring the Connections
Gum diseases, also known as periodontal diseases, are a group of conditions affecting the tissues that support and surround the teeth. These diseases range from simple gum inflammation to serious conditions that can result in major damage to the soft tissue and bone that support the teeth. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for gum diseases is crucial for maintaining oral health.
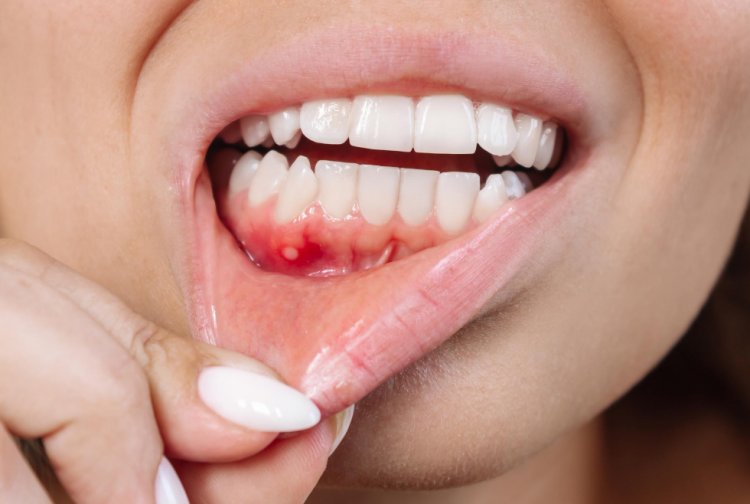
Causes of Gum Diseases:
Gum diseases are primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—on the teeth and gums. When plaque isn't properly removed through brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a professional dental cleaning. Tartar buildup irritates the gums, leading to inflammation and the development of gum diseases.
Other factors contributing to gum diseases include:
-
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up, increasing the risk of gum disease.
-
Tobacco Use: Smoking or chewing tobacco can significantly increase the risk of gum diseases.
-
Genetics: Some individuals may be more genetically predisposed to gum diseases.
-
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can make gums more susceptible to inflammation.
-
Certain Medications: Some medications can affect oral health by causing dry mouth or gum tissue changes.
-
Chronic Diseases: Conditions such as diabetes and HIV/AIDS can weaken the body's immune system, making gum disease more likely.
Symptoms of Gum Diseases:
The symptoms of gum diseases can vary depending on the severity of the condition but may include:
-
Gums that bleed easily: Healthy gums should not bleed during brushing or flossing.
-
Swollen or tender gums: Inflammation is a common sign of gum disease.
-
Persistent bad breath: Bacteria in plaque and tartar can produce foul odors.
-
Receding gums: Gums may pull away from the teeth, making the teeth appear longer.
-
Loose or shifting teeth: Advanced gum disease can cause tooth loss if left untreated.
-
Painful chewing: Discomfort while chewing can indicate gum disease or other oral health issues.
Treatment of Gum Diseases:
Treatment for gum diseases aims to control infection, reduce inflammation, and restore the health of the gums and supporting tissues. Common treatments include:
-
Professional Cleaning: Dental professionals can remove plaque and tartar from the teeth and gums through scaling and root planing procedures.
-
Medication: Antibacterial mouthwashes or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to control infection and inflammation.
-
Surgery: In severe cases of gum disease, surgical interventions such as flap surgery, bone grafts, or tissue grafts may be necessary to repair damaged tissues and promote healing.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Quitting smoking, improving oral hygiene practices, and managing underlying health conditions can help prevent gum diseases from recurring.
-
Regular Dental Checkups: Routine dental examinations and cleanings are essential for early detection and treatment of gum diseases.
Prevention of Gum Diseases:
Preventing gum diseases involves maintaining good oral hygiene habits and addressing risk factors:
-
Brushing and Flossing: Brush teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent tartar buildup.
-
Healthy Diet: Limit sugary foods and drinks, which can contribute to plaque formation, and eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
-
Regular Dental Visits: Schedule dental checkups and cleanings at least twice a year to monitor oral health and address any issues promptly.
-
Avoid Tobacco: Quit smoking or using tobacco products to reduce the risk of gum diseases and other oral health problems.
-
Manage Stress: Stress can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections, including gum diseases. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies.
In conclusion, gum diseases are common but preventable conditions that can have serious consequences if left untreated. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of gum diseases, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain optimal oral health and prevent complications.
#GumDiseases #PeriodontalHealth #OralHygiene #DentalCare #ToothDecay #OralHealth #Gingivitis #PlaqueBuildup #DentalTips #HealthySmile #PreventGumDisease #OralCare #GumHealth #DentalCheckup #DentalHygiene #SmileCare #HealthyTeeth #OralHealthTips #GumHealthMatters #DentalWellness
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
What's Your Reaction?





















