Building Stronger Bones: Strategies to Combat Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a common bone disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to an increased risk of fractures. It affects millions of people worldwide, particularly older adults, and poses significant health challenges. Understanding its symptoms, causes, treatment options, and preventive measures is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
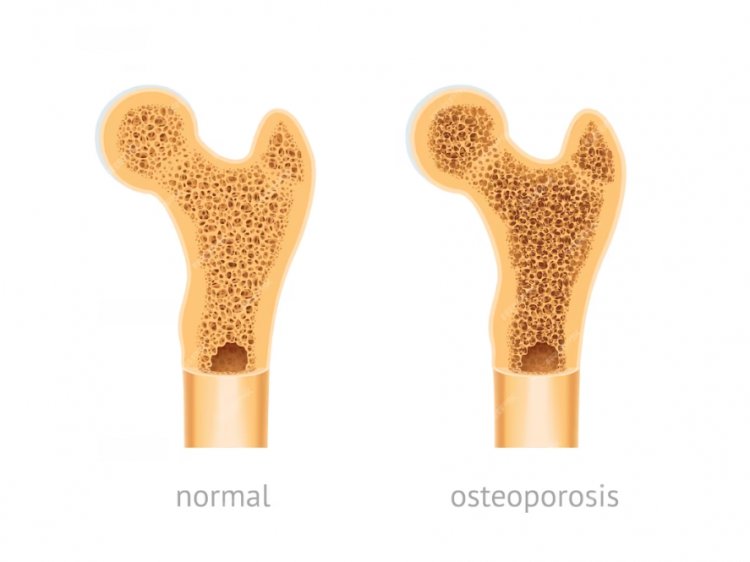
Symptoms:
- Fractures: Osteoporosis weakens bones, making them more susceptible to fractures, especially in the spine, hips, and wrists.
- Back Pain: Compression fractures in the spine can cause severe back pain, loss of height, and a stooped posture.
- Loss of Height: Osteoporosis-related vertebral fractures can result in a gradual loss of height over time.
- Bone Weakness: Bones become fragile and prone to fractures even with minor trauma or stress.
Causes:
- Aging: Aging is a significant risk factor for osteoporosis as bone mass decreases and bone turnover slows down.
- Hormonal Changes: Reduced estrogen levels in women post-menopause and low testosterone levels in men can contribute to bone loss.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of calcium, vitamin D, and other nutrients necessary for bone health can increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Lifestyle Factors: Lack of physical activity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle can weaken bones and exacerbate osteoporosis.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions such as hyperthyroidism, rheumatoid arthritis, and gastrointestinal disorders can interfere with bone metabolism and increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Medications: Long-term use of corticosteroids and some other medications can weaken bones and contribute to osteoporosis.
Diagnosis:
- Bone Density Testing: Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) is the most commonly used test to measure bone density and diagnose osteoporosis.
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will review your medical history, assess risk factors, and perform a physical examination to evaluate signs of bone loss or fractures.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood and urine tests may be conducted to assess bone turnover markers and rule out other medical conditions affecting bone health.
Treatment:
- Medications: Bisphosphonates, hormone therapy, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), and other medications may be prescribed to slow bone loss and reduce fracture risk.
- Calcium and Vitamin D Supplements: Adequate intake of calcium (1000-1200 mg/day) and vitamin D (800-1000 IU/day) is essential for maintaining bone health.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular weight-bearing exercises, such as walking or strength training, can help strengthen bones and improve balance. Quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and maintaining a healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin D are also important.
- Fall Prevention: Taking measures to prevent falls, such as removing tripping hazards at home, using handrails, and wearing appropriate footwear, can reduce the risk of fractures, especially in older adults.
Prevention:
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, protein, fruits, and vegetables promotes bone health.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises helps build and maintain bone density.
- Avoidance of Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Smoking cessation and moderation in alcohol consumption are crucial for preserving bone health.
- Bone Density Screening: Periodic bone density testing helps identify individuals at risk of osteoporosis and allows for early intervention.
- Medication Adherence: If prescribed medications for osteoporosis, it's important to take them as directed by your healthcare provider to maximize their effectiveness.
In conclusion, osteoporosis is a chronic condition that requires proactive management to prevent complications such as fractures and maintain quality of life. By understanding its symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options, individuals can take steps to preserve bone health and reduce the impact of osteoporosis on their lives. Consultation with healthcare professionals is essential for personalized assessment and management of this condition.
#OsteoporosisAwareness #BoneHealth #FractureRisk #HealthyBones #OsteoporosisPrevention #BoneDensity #StrongBones #OsteoporosisTreatment #HealthTips #AgingWell #PreventFalls #HealthyLifestyle #CalciumVitaminD #FitnessForBones #HealthyDiet #MedicalAdvice #HealthcareConsultation
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
What's Your Reaction?





















