Mental Health Matters: Exploring the Depths of Well-being
Mental health is an integral and essential component of overall health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), mental health is defined as "a state of well-being in which every individual realizes his or her own potential, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to her or his community." This definition highlights the importance of mental health in achieving a balanced and fulfilling life.
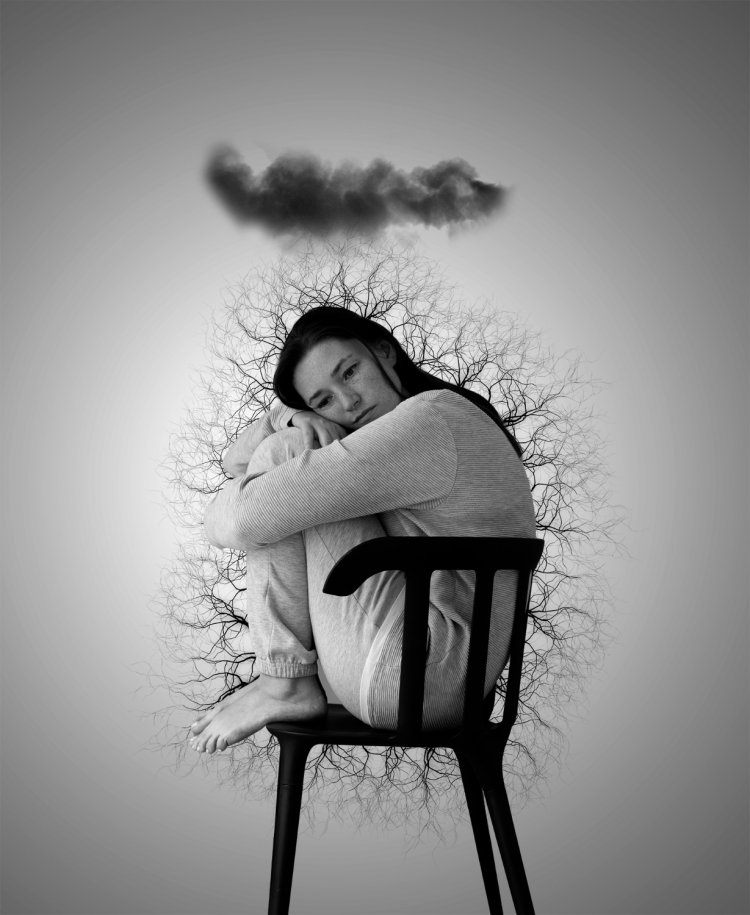

The Importance of Mental Health
Mental health affects how we think, feel, and act. It also helps determine how we handle stress, relate to others, and make choices. At every stage of life, from childhood and adolescence through adulthood, mental health plays a critical role. Good mental health is not just the absence of mental illness; it is about being cognitively, emotionally, and socially healthy.
Mental health is crucial because it:
Enhances Quality of Life
Good mental health contributes to a better quality of life by enabling individuals to manage stress, work productively, and enjoy fulfilling relationships.
Improves Physical Health
Mental health has a direct impact on physical health. Chronic stress and anxiety can lead to physical health problems such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and weakened immune function.
Promotes Healthy Relationships
Mental well-being fosters positive relationships by enhancing communication, empathy, and emotional connection.
Facilitates Productivity
Good mental health enhances cognitive function, concentration, and productivity, which are essential for personal and professional success.
Common Mental Health Disorders
Depression
Depression is a common and serious medical illness that negatively affects how you feel, the way you think, and how you act. It causes feelings of sadness and/or a loss of interest in activities once enjoyed. Symptoms can vary from mild to severe and can include:
- Feeling sad or having a depressed mood
- Loss of interest or pleasure in activities once enjoyed
- Changes in appetite—weight loss or gain unrelated to dieting
- Trouble sleeping or sleeping too much
- Loss of energy or increased fatigue
- Increase in purposeless physical activity or slowed movements and speech
- Feeling worthless or guilty
- Difficulty thinking, concentrating, or making decisions
- Thoughts of death or suicide
Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are the most common mental health disorders in the United States, affecting 40 million adults in the U.S. aged 18 and older, or 18.1% of the population every year. Types of anxiety disorders include:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Excessive, uncontrollable worry about various aspects of life.
- Panic Disorder: Recurrent, unexpected panic attacks and the fear of experiencing another attack.
- Social Anxiety Disorder: Intense fear of social situations where one may be judged or scrutinized by others.
- Specific Phobias: Intense fear of specific objects or situations, such as heights or flying.
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is characterized by extreme mood swings that include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression). Symptoms of mania can include:
- Elevated mood
- Increased activity, energy, or agitation
- Exaggerated sense of well-being and self-confidence
- Decreased need for sleep
- Unusual talkativeness
- Racing thoughts
- Distractibility
- Poor decision-making
During depressive episodes, individuals may experience symptoms of depression similar to those mentioned above.
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with schizophrenia may seem like they have lost touch with reality. Symptoms include:
- Hallucinations: Seeing or hearing things that are not present.
- Delusions: Strongly held false beliefs not influenced by reality.
- Disorganized Thinking: Incoherent speech and thought processes.
- Abnormal Motor Behavior: This can include catatonia, or excessive movement.
- Negative Symptoms: Reduced ability to function normally, such as lack of emotion or social withdrawal.
Factors Affecting Mental Health
Biological Factors
Biological factors, including genetics and neurochemistry, play a significant role in mental health. Mental health disorders often run in families, indicating a hereditary component. For example, if a parent has depression, their child is more likely to develop depression. Neurotransmitter imbalances, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, are also associated with various mental health conditions.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors, including trauma, abuse, and significant life changes, can significantly impact mental health. Early childhood experiences, such as neglect, abuse, and loss, can have long-lasting effects on mental health. Stressful life events, such as losing a loved one, divorce, or financial difficulties, can trigger or exacerbate mental health disorders.
Social Factors
Social factors, such as poverty, social isolation, and discrimination, can have a profound effect on mental health. Living in a safe and supportive community with access to healthcare, education, and employment opportunities promotes mental well-being. Conversely, environments characterized by violence, inequality, and lack of resources can contribute to mental health problems.
Promoting Mental Health
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, and getting adequate sleep are crucial for mental health. Exercise releases endorphins, which are chemicals in the brain that act as natural painkillers and mood elevators. A nutritious diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, can help maintain overall well-being. Sleep is essential for mental and emotional resilience, and a lack of sleep can contribute to mental health issues.
Stress Management Techniques
Learning how to manage stress is vital for maintaining good mental health. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and improve mental health. Mindfulness involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment, which can help individuals manage stress and negative emotions. Meditation practices, such as deep breathing exercises and guided imagery, can promote relaxation and mental clarity. Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to enhance physical and mental well-being.
Seeking Professional Help
If you or someone you know is experiencing mental health issues, it is important to seek professional help. Psychologists, psychiatrists, and counselors can provide therapy and medication to help manage mental health disorders. Various therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and psychodynamic therapy, can be effective in treating mental health conditions. Early intervention can prevent mental health issues from worsening and improve outcomes.
Building Strong Relationships
Having a strong support network can significantly improve mental health. Building and maintaining healthy relationships with family, friends, and colleagues can provide emotional support and reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation. Social connections offer a sense of belonging and purpose, which are important for mental well-being. Engaging in community activities, volunteering, and joining support groups can also foster social connections and enhance mental health.
Practicing Self-Care
Practicing self-care is essential for maintaining good mental health. Self-care involves taking time to engage in activities that bring joy, relaxation, and fulfillment. This can include hobbies, reading, spending time in nature, or engaging in creative pursuits. Setting boundaries and prioritizing self-care can help individuals manage stress and prevent burnout.
In conclusion, mental health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being that affects every aspect of our lives. Understanding the importance of mental health, recognizing the signs of mental health disorders, and knowing when and how to seek help are essential steps in promoting mental well-being. By adopting healthy lifestyle choices, managing stress effectively, and building strong relationships, individuals can improve their mental health and lead more fulfilling lives. It is important to remember that mental health is a journey, and seeking help and support is a sign of strength, not weakness.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
#MentalHealth #WellBeing #Depression #Anxiety #SelfCare #MentalHealthAwareness #StressManagement #HealthyLifestyle #SeekingHelp #MentalHealthMatters
What's Your Reaction?