Unveiling Spider Veins: Understanding Telangiectasia
Telangiectasia, commonly known as spider veins, refers to the small, dilated blood vessels that appear near the surface of the skin or mucous membranes. These red, blue, or purple lines can manifest anywhere on the body but are most frequently observed on the face, legs, and chest. While often considered a cosmetic concern, telangiectasia can sometimes be a symptom of underlying medical conditions. This comprehensive article delves into the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of telangiectasia.
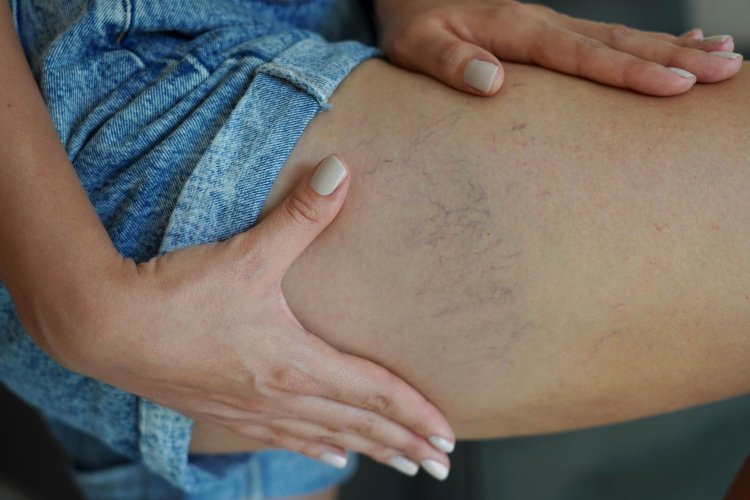
Causes of Telangiectasia
The development of telangiectasia can be attributed to a variety of factors, ranging from genetic predispositions to environmental influences and medical conditions. The primary causes include:
Genetic Factors
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)
An inherited disorder that leads to abnormal blood vessel formation and can cause bleeding in various parts of the body.
Other Genetic Conditions
Genetic predispositions can make individuals more susceptible to developing telangiectasia without a specific identifiable cause.
Chronic Sun Exposure
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation
Prolonged exposure to the sun’s UV rays can damage the skin and the small blood vessels beneath it, leading to the appearance of telangiectasia.
Photodamage
Sun-induced skin damage, known as photodamage, can exacerbate the formation of these visible blood vessels.
Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can lead to the dilation of blood vessels.
Menopause
Hormonal shifts during menopause can contribute to the appearance of telangiectasia.
Contraceptive Use
Hormonal contraceptives can also play a role in the development of spider veins.
Medical Conditions
Rosacea
A chronic skin condition that often causes redness and visible blood vessels on the face.
Scleroderma
A group of autoimmune diseases that cause hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues, often leading to telangiectasia.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
An autoimmune disease that can cause inflammation and damage to various body systems, including the skin.
Lifestyle Factors
Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol intake can cause blood vessels to dilate and become more visible.
Environmental Toxins
Exposure to harmful environmental substances can damage blood vessels.
Long-term Use of Corticosteroids
These medications can thin the skin and make blood vessels more apparent.
Diagnosis of Telangiectasia
The diagnosis of telangiectasia involves a multifaceted approach to ensure accurate identification and to rule out underlying conditions. The diagnostic process typically includes:
Clinical Examination
A dermatologist or healthcare provider will visually inspect the skin to identify the presence and pattern of dilated blood vessels. The extent and distribution of the telangiectasia are assessed to guide further evaluation.
Medical History
A detailed review of the patient’s medical history, including any family history of similar conditions, is conducted to identify potential genetic factors. Information on lifestyle habits, such as sun exposure and alcohol consumption, is gathered.
Dermatoscopy
This non-invasive technique uses a specialized magnifying instrument to provide a detailed view of the skin and underlying blood vessels. Dermatoscopy helps in distinguishing telangiectasia from other vascular lesions.
Blood Tests
Blood tests may be ordered to check for systemic diseases or conditions that could be contributing to the appearance of telangiectasia. These tests help identify autoimmune diseases, liver function abnormalities, and other potential underlying issues.
Imaging Studies
In cases where systemic involvement is suspected, imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans may be used to investigate further. These imaging techniques help in assessing internal organ involvement and other systemic effects.
Treatment of Telangiectasia
The treatment of telangiectasia is tailored to the severity of the condition, the underlying causes, and the patient’s preferences. Available treatments range from conservative measures to advanced medical procedures:
Topical Treatments
Retinoids
Creams and ointments containing retinoids can enhance skin cell turnover and promote collagen production, helping to reduce the visibility of telangiectasia.
Anti-inflammatory Creams
Topical anti-inflammatory agents can help manage associated symptoms, such as redness and irritation.
Laser Therapy
Pulsed Dye Lasers (PDL)
These lasers target the hemoglobin in blood vessels, causing them to coagulate and be absorbed by the body.
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL)
IPL uses broad-spectrum light to treat a variety of skin conditions, including telangiectasia, by targeting the blood vessels beneath the skin.
Sclerotherapy
This procedure involves injecting a sclerosing solution directly into the affected veins, causing them to collapse and be reabsorbed by the body over time. Sclerotherapy is particularly effective for telangiectasia on the legs.
Electrosurgery
Electrosurgery employs electrical currents to coagulate and eliminate the abnormal blood vessels. This technique is often used for smaller, more localized areas of telangiectasia.
Lifestyle Changes
Sun Protection
Using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing can prevent further damage from UV radiation.
Alcohol Reduction
Reducing alcohol intake can help decrease the prominence of dilated blood vessels.
Healthy Skin Care
Adopting a skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing and moisturizing can support overall skin health.
Medical Management
For telangiectasia related to underlying medical conditions, treating the primary disease is crucial. Management of conditions like rosacea or scleroderma involves a combination of medications and lifestyle adjustments to control symptoms and prevent progression.
Telangiectasia, while often perceived as a cosmetic issue, can sometimes signal more serious underlying health concerns. Understanding the diverse causes, obtaining an accurate diagnosis, and exploring the appropriate treatment options are essential steps in managing this condition effectively. If you notice the development of spider veins or related symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action. Advances in medical technology and a deeper understanding of telangiectasia now provide effective options for management and treatment, ensuring better outcomes for those affected.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
Hashtags
#Telangiectasia #Health #SkinCare #MedicalAdvice #Diagnosis #Treatment #HealthTips
What's Your Reaction?





















