Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Among its various forms, Type 1 diabetes is a unique and complex disorder that requires careful management and understanding. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of Type 1 diabetes, exploring its causes, symptoms, and strategies for effective management.
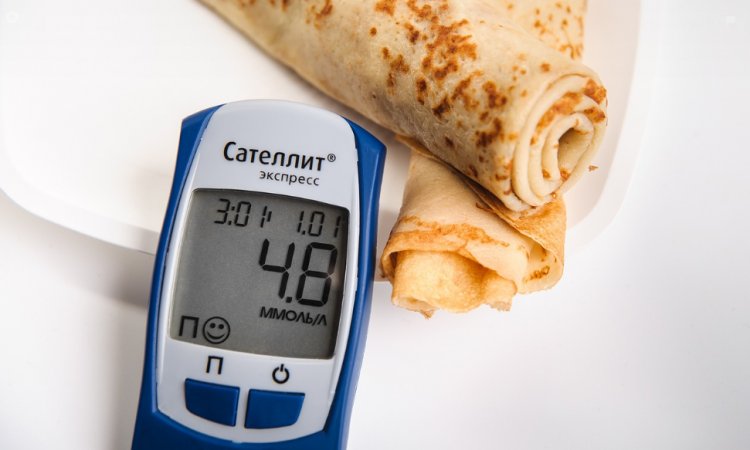
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes, formerly known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar (glucose) levels in the body. Without sufficient insulin, glucose cannot enter cells to provide energy, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes:
The exact cause of Type 1 diabetes is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors. Individuals with certain genetic markers are more susceptible to developing Type 1 diabetes, but environmental triggers, such as viral infections or exposure to certain toxins, may also play a role in triggering the autoimmune response against beta cells.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes:
The onset of Type 1 diabetes can be rapid and dramatic, with symptoms often appearing suddenly. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination: Excess glucose in the blood pulls water from tissues, leading to increased urination.
- Excessive Thirst: Dehydration resulting from frequent urination triggers intense thirst.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Without adequate insulin, the body begins to break down muscle and fat for energy, causing weight loss.
- Increased Hunger: Despite eating regularly, individuals may experience persistent hunger due to the body's inability to utilize glucose for energy.
- Fatigue: Insufficient glucose in cells leads to fatigue and weakness, even with adequate rest.
If left untreated, Type 1 diabetes can progress to more severe symptoms, including blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, and even diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a life-threatening condition characterized by high blood sugar levels and the presence of ketones in the blood.
Management of Type 1 Diabetes:
While there is currently no cure for Type 1 diabetes, effective management strategies can help individuals lead healthy and fulfilling lives. Key components of diabetes management include:
- Insulin Therapy: Since Type 1 diabetes results from a lack of insulin production, insulin replacement therapy is essential. This typically involves multiple daily injections of insulin or the use of an insulin pump to deliver insulin continuously.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is critical for adjusting insulin doses and preventing complications. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems provide real-time glucose readings, helping individuals make informed decisions about insulin therapy and lifestyle choices.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help stabilize blood sugar levels and promote overall health. Carbohydrate counting and meal planning are often used to regulate glucose levels.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps control blood sugar levels. Incorporating regular exercise into daily routines can also reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
- Education and Support: Education about diabetes self-management and access to support networks are crucial for empowering individuals with Type 1 diabetes to effectively manage their condition. Diabetes educators, support groups, and online resources can provide valuable information and encouragement.
In conclusion, Type 1 diabetes is a complex autoimmune disease that requires lifelong management. By understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and implementing effective management strategies, individuals with Type 1 diabetes can achieve optimal health and well-being despite the challenges posed by this condition.
Clinics in The United Kingdom:
- NHS (National Health Service) Trust Hospitals - NHS hospitals have specialized units for the diagnosis and treatment of Type 1 Diabetes.
- King's College Hospital, London - Offers diagnosis and treatment for Type 1 Diabetes by endocrinology and diabetes specialists.
- Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge - A center providing high-quality diabetes care and treatment.
- Manchester Diabetes Centre - Located in Manchester, this center offers a wide range of services for Type 1 Diabetes patients.
- Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh - A leading center in Edinburgh for the diagnosis and treatment of Type 1 Diabetes.
Clinics in Turkey:
- Hacettepe University Hospital, Ankara - Provides diagnosis and treatment for Type 1 Diabetes through its endocrinology department.
- Dokuz Eylül University Faculty of Medicine Hospital, Izmir - The endocrinology and metabolism department serves Type 1 Diabetes patients.
- Istanbul University Cerrahpaşa Faculty of Medicine, Istanbul - A hospital with specialized units for the diagnosis and treatment of Type 1 Diabetes.
- Ankara City Hospital, Ankara - Offers services to Type 1 Diabetes patients through its diabetes outpatient clinic.
- Acıbadem Hospital, Istanbul - Endocrinology and metabolism specialists here have experience in the diagnosis and treatment of Type 1 Diabetes.

Discover Coupoly's exclusive Medical Concierge Service, connecting you with renowned doctors and clinics, alongside our complimentary Travel Concierge Service, linking you with top UK travel agencies.
Contact us now to learn more.
Get in Touch
What's Your Reaction?





















