Tonsillectomy: A Comprehensive Overview of Surgical Removal of Tonsils
Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure aimed at removing the tonsils, which are lymphoid tissues located at the back of the throat. This procedure is commonly performed to alleviate chronic or recurrent infections, manage obstructive sleep apnea, or address other complications related to the tonsils.
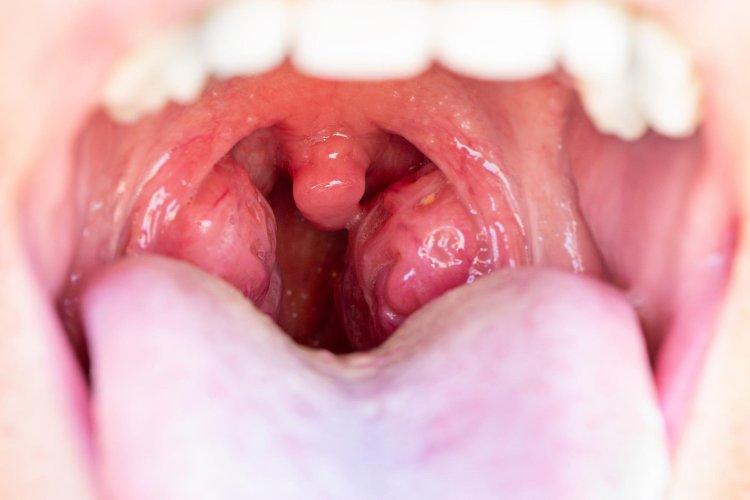
Indications for Tonsillectomy
Chronic Tonsillitis
- Definition: Recurrent bacterial or viral infections of the tonsils leading to sore throat, fever, and swollen glands.
- Frequency: Typically considered if a patient experiences multiple episodes per year despite antibiotic therapy.
- Impact: Chronic tonsillitis can significantly impair daily activities and quality of life.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
- Mechanism: Enlarged tonsils can obstruct the airway during sleep, leading to disrupted breathing patterns and decreased oxygen levels.
- Symptoms: Includes snoring, restless sleep, daytime fatigue, and in severe cases, cardiovascular complications.
- Management: Tonsillectomy can be curative in cases where enlarged tonsils contribute to OSA.
Peritonsillar Abscess
- Occurrence: A localized collection of pus behind the tonsil, often necessitating drainage and subsequent consideration for tonsillectomy to prevent recurrence.
Pre-operative Preparation
Evaluation
- Medical History: Review of symptoms, frequency of infections, and previous treatments.
- Physical Examination: Assessment of the size and condition of the tonsils.
- Imaging Studies: Occasionally, CT scans or X-rays may be used to evaluate the extent of tonsillar enlargement or complications.
Anesthesia Considerations
- General Anesthesia: Most tonsillectomies are performed under general anesthesia to ensure patient comfort and safety throughout the procedure.
Surgical Technique
Access and Exposure
- Positioning: The patient is placed supine with the neck extended.
- Mouth Opening: A mouth gag or retractor is used to provide optimal exposure of the tonsils.
Tonsil Removal
- Tools: Surgical techniques may include cold steel dissection, electrocautery, coblation, or harmonic scalpel.
- Technique: The tonsils are carefully dissected away from their surrounding tissues and removed.
Hemostasis and Closure
- Control of Bleeding: Bleeding vessels are cauterized or ligated to minimize post-operative bleeding.
- Closure: In most cases, the tonsillar beds are left to heal naturally without the need for sutures.
Post-operative Care
Recovery Room Monitoring
- Vital Signs: Close monitoring of vital signs and emergence from anesthesia.
- Pain Management: Administration of pain medications as needed.
Home Care Instructions
- Dietary Restrictions: Initially, a soft diet is recommended to prevent trauma to the healing surgical site.
- Activity Restrictions: Avoidance of strenuous activities to minimize the risk of bleeding.
Follow-up Visits
- Evaluation: Scheduled visits with the surgeon to monitor healing and address any concerns.
- Resumption of Normal Activities: Guidance on when to resume normal activities, including school or work.
Potential Complications
Bleeding
- Risk: Most common within the first 24 hours post-surgery.
- Management: Requires prompt assessment and intervention to prevent significant blood loss.
Infection
- Risk: Possibility of wound infection or secondary infections despite prophylactic antibiotics.
Pain and Discomfort
- Duration: Variable, typically improving within 7-10 days post-surgery with appropriate pain management.
Rare Complications
- Damage to Adjacent Structures: Including the uvula, palate, or lingual nerves.
- Anesthesia-related Risks: Adverse reactions or complications related to general anesthesia.
Tonsillectomy remains a widely performed surgical procedure with significant benefits for patients suffering from chronic tonsillitis, obstructive sleep apnea, or peritonsillar abscess. While the decision to proceed with tonsillectomy involves weighing potential risks against benefits, it is generally regarded as safe and effective in improving quality of life and reducing recurrent infections. Consultation with an experienced ENT specialist is crucial to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual medical needs and preferences.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
#Tonsillectomy #ChronicTonsillitis #ObstructiveSleepApnea #PeritonsillarAbscess #Surgery #ENT #HealthCare #MedicalAdvice
What's Your Reaction?





















