Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Guide to the Chronic Skin Condition
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by raised, red, scaly patches on the skin's surface, psoriasis can significantly impact an individual's physical and emotional well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate aspects of psoriasis, including its causes, symptoms, types, treatment options, and the latest research developments.
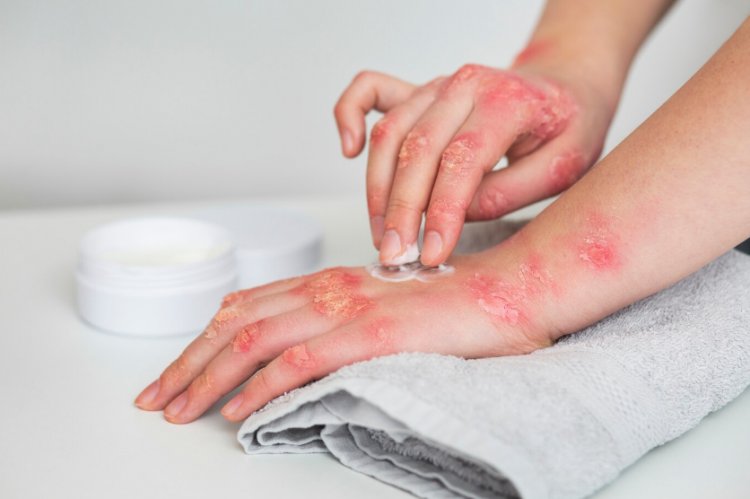
Understanding Psoriasis: Psoriasis is a multifactorial condition involving genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and dysregulated immune responses. The hallmark feature of psoriasis is the rapid turnover of skin cells, resulting in the accumulation of thick, scaly plaques. These plaques can appear anywhere on the body, including the scalp, elbows, knees, lower back, and nails. Psoriasis is associated with various comorbidities, including psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and mental health disorders.
Causes and Triggers: The exact cause of psoriasis is complex and not fully understood, but it is believed to involve genetic predisposition combined with environmental factors and immune dysregulation. Common triggers for psoriasis flare-ups include stress, infections (such as streptococcal throat infections), injury to the skin (such as cuts, scratches, or sunburn), certain medications (such as beta-blockers or lithium), smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Types of Psoriasis: Psoriasis manifests in several clinical forms, each with its own distinct characteristics:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, characterized by raised, red plaques covered with silvery scales.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Small, drop-like lesions that often appear suddenly, usually after a bacterial or viral infection.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Smooth, red patches that develop in skin folds, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts.
- Pustular Psoriasis: White, pus-filled blisters surrounded by red skin, typically on the hands and feet.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: A type of inflammatory arthritis that affects some individuals with psoriasis, causing joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Treatment Options: While there is currently no cure for psoriasis, various treatment modalities can effectively manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Topical Treatments: Corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, retinoids, coal tar preparations, and moisturizers.
- Phototherapy: Ultraviolet (UV) light therapy, including narrowband UVB, broadband UVB, and psoralen plus UVA (PUVA) therapy.
- Systemic Medications: Oral or injectable medications, such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, acitretin, apremilast, and oral or biologic agents (such as TNF-alpha inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors, IL-23 inhibitors, and IL-12/23 inhibitors).
- Combination Therapies: Combining different treatment modalities for enhanced efficacy, such as phototherapy with topical treatments or systemic medications with biologic agents.
Latest Research and Developments: Ongoing research in psoriasis aims to deepen our understanding of the underlying pathophysiology and develop novel therapeutic approaches:
- Genetic Studies: Investigating the role of genetic variants in psoriasis susceptibility and disease severity.
- Immunological Research: Exploring immune pathways involved in psoriasis inflammation and identifying potential therapeutic targets.
- Biologic Therapies: Developing next-generation biologic agents with improved efficacy, safety profiles, and modes of administration.
- Personalized Medicine: Advancing precision medicine approaches to tailor treatment strategies based on individual patient characteristics, including genetic, immunological, and clinical factors.
Conclusion: Psoriasis is a complex and multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. By understanding its underlying causes, clinical manifestations, treatment options, and ongoing research efforts, healthcare professionals and individuals living with psoriasis can collaborate to develop personalized treatment plans that optimize outcomes and improve quality of life.
Clinics in UK:
- St John's Institute of Dermatology - Psoriasis Clinic, London
- The Psoriasis Association Clinic - Leeds
- The London Dermatology Centre - Psoriasis Treatment Services
- Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust - Dermatology Department
- The Dermatology Clinic - Manchester Royal Infirmary
Clinics in Turkey:
- Istanbul Florence Nightingale Hospital - Dermatology Department
- Acıbadem Healthcare Group - Dermatology Clinic
- Memorial Hospital - Psoriasis Treatment Center
- Istanbul University Cerrahpaşa Faculty of Medicine - Dermatology Department
- Ankara University Faculty of Medicine - Dermatology Clinic
Discover Coupoly's exclusive Medical Concierge Service, connecting you with renowned doctors and clinics, alongside our complimentary Travel Concierge Service, linking you with top UK travel agencies.
Contact us now to learn more.
Get in Touch
What's Your Reaction?





















