Impetigo in Children: What Parents Need to Know
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection primarily affecting infants and young children, though it can occur at any age. Characterized by red sores around the nose, mouth, hands, and feet, these sores burst and develop honey-colored crusts, making the condition easily identifiable.
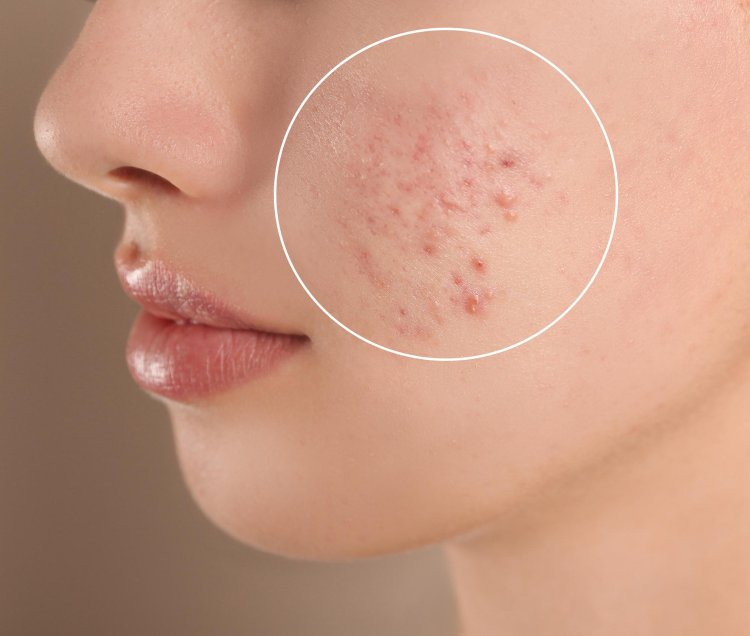
How Does Impetigo Develop?
Impetigo develops when bacteria enter the skin through cuts, abrasions, insect bites, or other skin injuries. The main bacteria responsible are:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pyogenes
Once these bacteria infect the skin, they proliferate, causing the characteristic sores of impetigo. The infection can spread through direct contact with the sores or by touching contaminated items such as towels, clothing, or toys.
Types of Impetigo
Non-bullous Impetigo (Crusted Impetigo)
- Description: The most common form, accounting for about 70% of cases.
- Appearance: Begins as red sores around the nose and mouth, which burst and form a yellowish-brown crust. These sores may be itchy and painful.
Bullous Impetigo
- Description: Less common, primarily affects infants and young children.
- Appearance: Large, fluid-filled blisters that can appear on various body parts, including the trunk, arms, and legs. These blisters are less likely to burst compared to the sores of non-bullous impetigo.
Symptoms of Impetigo
- Red Sores: These quickly rupture, ooze for a few days, and then form a yellowish-brown crust.
- Itching and Soreness: Affected areas can be itchy and tender.
- Fluid-filled Blisters: Especially in bullous impetigo.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: In severe cases, nearby lymph nodes may become swollen.
Causes of Impetigo
Impetigo is primarily caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. Contributing factors include:
- Direct Contact: With an infected person.
- Poor Hygiene: Increases susceptibility to infection.
- Climate: Warm and humid environments favor bacterial growth.
- Skin Injuries: Minor cuts, abrasions, or insect bites.
- Underlying Skin Conditions: Such as eczema or dermatitis.
Diagnosis of Impetigo
Diagnosis is generally based on the visual examination of the sores. However, in cases where the infection does not respond to initial treatment, a swab of the affected area might be taken to identify the specific bacteria involved, guiding appropriate antibiotic therapy.
Treatment Methods for Impetigo
Effective treatment aims to clear the infection and prevent its spread:
Topical Antibiotics
- Examples: Mupirocin, retapamulin.
- Usage: Applied directly to the sores, usually for a period of 5 to 10 days.
Oral Antibiotics
- Examples: Dicloxacillin, cephalexin, clindamycin.
- Usage: Prescribed for more severe or widespread infections, or when topical treatment is ineffective.
Additional care includes keeping the affected area clean and covered to prevent the spread of bacteria.
Preventing Impetigo
To reduce the risk of contracting impetigo:
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing with soap and water.
- Avoid Contact: With infected individuals.
- Keep Wounds Clean: Clean and cover cuts, scrapes, and insect bites.
- Do Not Share Personal Items: Such as towels, clothing, or razors.
- Disinfect Surfaces: Clean objects and surfaces that may be contaminated.
Risk Factors for Contracting Impetigo
Certain factors increase the risk of developing impetigo:
- Age: Children aged 2-5 are most susceptible due to close contact in school and daycare settings.
- Environment: Warm, humid climates.
- Activities: Contact sports increase the risk due to skin-to-skin contact.
- Existing Skin Conditions: Conditions like eczema that compromise the skin barrier.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with a weakened immune system are at higher risk.
In conclusion, impetigo is a common and highly contagious skin infection that can be effectively managed with appropriate medical treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, preventive measures, and risk factors is crucial for managing and reducing the spread of this infection. Good hygiene practices and timely medical intervention are essential for a quick recovery and preventing further transmission.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
Hashtags
#Impetigo #SkinInfection #Health #MedicalAdvice #Hygiene #BacterialInfection #SkinCare #ChildHealth #InfectionPrevention
What's Your Reaction?





















