Hernia Alert: Detecting and Defeating Inguinal Hernias
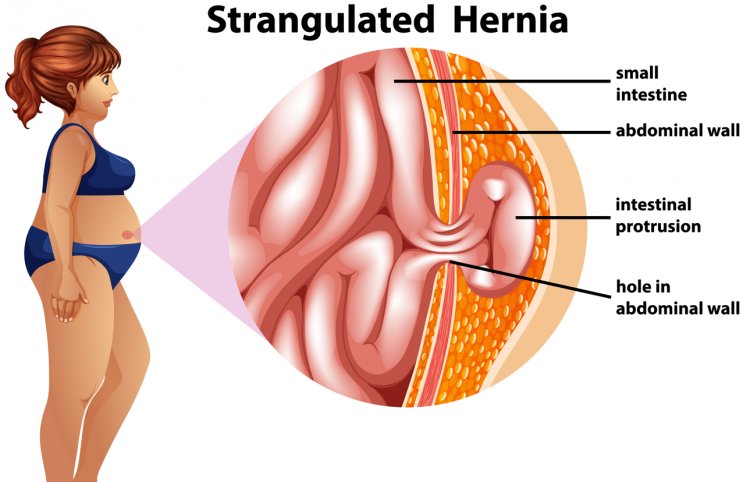
An inguinal hernia is a common medical condition where soft tissue, usually a portion of the intestine, protrudes through a weak spot or tear in the abdominal wall muscles. This protrusion typically manifests as a noticeable bulge in the groin area. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of inguinal hernias, covering everything from their definition to treatment options and preventive measures.
What is an Inguinal Hernia?
An inguinal hernia occurs when a portion of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weakened area in the abdominal wall, particularly in the inguinal canal. This canal is situated in the groin region and is a common site for hernias to develop.
Symptoms of Inguinal Hernia
The symptoms of an inguinal hernia may vary depending on the size and severity of the hernia. Common symptoms include:
- Visible bulge: The most apparent sign of an inguinal hernia is a bulge in the groin area, which may become more prominent when standing, coughing, or straining.
- Discomfort or pain: Individuals with inguinal hernias often experience discomfort or a dull ache in the groin, particularly during activities such as lifting heavy objects or bending over.
- Weakness or pressure: Some people may feel weakness or pressure in the groin, accompanied by a dragging sensation.
- Burning or tingling: Inguinal hernias can cause a burning or tingling sensation around the bulge site, which may worsen with prolonged standing or physical exertion.
Causes of Inguinal Hernia
Several factors can contribute to the development of inguinal hernias, including:
- Weak abdominal muscles: Congenital weaknesses in the abdominal wall muscles, present since birth, can predispose individuals to inguinal hernias.
- Increased abdominal pressure: Activities that exert pressure on the abdominal wall, such as heavy lifting, chronic coughing, or straining during bowel movements, can weaken the muscles and lead to herniation.
- Age-related changes: As individuals age, their abdominal muscles may naturally weaken, increasing the risk of hernias.
- Previous surgeries: Prior abdominal surgeries, especially those involving incisions in the abdominal wall, can create weak spots that are susceptible to herniation.
Types of Inguinal Hernia
Inguinal hernias are classified into two main types:
- Direct inguinal hernia: This type occurs when abdominal contents protrude through a weakened area in the abdominal wall, typically in the inguinal canal. Direct inguinal hernias often present as bulges in the groin area.
- Indirect inguinal hernia: An indirect inguinal hernia develops when abdominal contents, usually the intestine, protrude through the inguinal ring, a natural passageway in the abdominal wall. Indirect hernias may extend into the scrotum in males.
Diagnosis of Inguinal Hernia
Diagnosing an inguinal hernia typically involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider. During the examination, the physician may ask the patient to cough or strain, which can make the hernia more noticeable. Imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the hernia.
Treatment Options for Inguinal Hernia
The treatment approach for inguinal hernias depends on several factors, including the size of the hernia, the presence of symptoms, and the individual's overall health. Treatment options include:
- Watchful waiting: If the hernia is small and not causing any symptoms, a healthcare provider may recommend a wait-and-see approach, with regular monitoring to detect any changes.
- Hernia truss: A hernia truss is a supportive device worn over the groin to help keep the hernia reduced. While it may provide temporary relief, it's not typically recommended for long-term use and may increase the risk of complications.
- Surgery: Most inguinal hernias require surgical repair to prevent complications such as incarceration or strangulation, where the protruding tissue becomes trapped and blood flow is compromised. The surgical approach may involve open or laparoscopic techniques, where the weakened abdominal wall is reinforced with stitches or mesh.
Prevention of Inguinal Hernia
While it's not always possible to prevent inguinal hernias, certain measures can help reduce the risk of their development. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can strain the abdominal muscles, increasing the risk of hernias.
- Avoiding heavy lifting: Minimize activities that require heavy lifting or straining, and practice proper lifting techniques when necessary.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking can weaken the abdominal muscles and impair tissue healing, making individuals more susceptible to hernias.
- Treating underlying conditions: Addressing chronic coughing or constipation promptly can help reduce strain on the abdominal wall.
In conclusion, an inguinal hernia occurs when abdominal tissue protrudes through a weakened area in the abdominal wall, resulting in a visible bulge in the groin area. While some hernias may be asymptomatic and require no immediate treatment, most necessitate surgical repair to prevent complications. Individuals can reduce their risk of inguinal hernias by adopting healthy lifestyle habits and minimizing factors that contribute to abdominal strain. If you suspect you have an inguinal hernia or experience symptoms suggestive of one, it's essential to seek prompt medical evaluation and appropriate management.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
Hashtags: #InguinalHernia #HerniaSymptoms #HerniaCauses #HerniaTypes #HerniaDiagnosis #HerniaTreatment #HerniaPrevention #HealthTips #MedicalAdvice
What's Your Reaction?