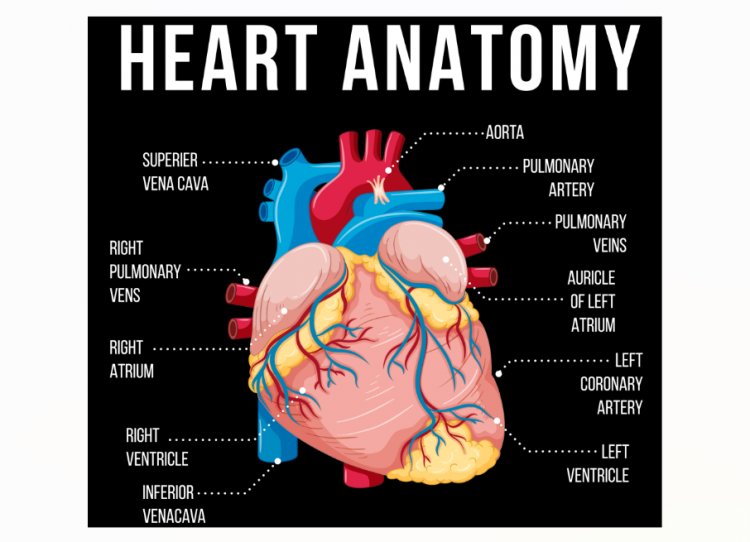
Symptoms of Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) encompass a broad range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. Common symptoms include:
Chest Pain or Discomfort
Often a sign of angina or heart attack.
Shortness of Breath
Can indicate heart failure or other heart conditions.
Palpitations
Irregular heartbeats that can be alarming.
Weakness or Dizziness
May result from inadequate blood flow to the brain.
Swelling in Legs, Ankles, and Feet
Known as edema, often associated with heart failure.
Fatigue
Persistent tiredness can be a symptom of various heart conditions.
Symptoms can vary widely depending on the specific cardiovascular condition, such as coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, or heart failure.
Causes of Cardiovascular Diseases
Several factors contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases:
Atherosclerosis
The accumulation of plaques in the arteries, which can restrict blood flow.
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Can damage blood vessels and the heart over time.
Smoking
A major risk factor that accelerates the process of atherosclerosis and damages blood vessels.
Diabetes
Poorly controlled blood sugar levels can harm the cardiovascular system.
Obesity
Excess weight increases the strain on the heart and can lead to other risk factors like hypertension and diabetes.
Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of physical activity contributes to several cardiovascular risk factors.
Genetics
Family history can increase susceptibility to heart disease.
Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease
The risk of developing cardiovascular disease varies based on several factors:
Age
The risk increases with age.
Gender
Men have a higher risk at a younger age, while women's risk increases post-menopause.
Family History
Genetics play a significant role in cardiovascular risk.
Lifestyle
Diet, physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption are critical factors.
Medical Conditions
Conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol elevate the risk.
Cardiovascular Disease Risk During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can pose unique cardiovascular risks due to the increased demands on the heart and changes in blood volume. Key concerns include:
Pre-eclampsia
Characterized by high blood pressure and potential organ damage.
Gestational Hypertension
High blood pressure that develops during pregnancy.
Peripartum Cardiomyopathy
A rare type of heart failure occurring in the final month of pregnancy or within five months postpartum.
Monitoring and managing these conditions are crucial for the health of both the mother and the baby.
Who Is at Risk for Cardiovascular Diseases?
Individuals at an increased risk for cardiovascular diseases include:
Family History
Those with a family history of heart disease.
Smokers
Tobacco users are at a significantly higher risk.
Chronic Conditions
People with diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol.
Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of physical activity increases risk.
Diet
Poor dietary habits, particularly high in saturated fats and sugars.
Older Adults
Age is a major risk factor.
Post-menopausal Women
Their risk increases after menopause due to hormonal changes.
Preventing Cardiovascular Diseases
Preventing cardiovascular diseases involves adopting healthy lifestyle practices and medical management:
Healthy Diet
Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Reduce salt, sugar, and saturated fats.
Regular Exercise
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity weekly.
Quit Smoking
Stopping smoking dramatically reduces cardiovascular risk.
Limit Alcohol
Drink in moderation – up to one drink per day for women and two for men.
Manage Stress
Employ stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation.
Regular Health Screenings
Monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar regularly.
Medications
Follow prescribed treatments for managing conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
Understanding cardiovascular health and implementing preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, leading to healthier, longer lives.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
Hashtags
#CardiovascularHealth #HeartDisease #HealthyLiving #Prevention #MedicalAdvic