From Diagnosis to Management: Living with Vasculitis
What is Vasculitis? Vasculitis is a group of disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels. This inflammation can lead to the weakening, thickening, narrowing, or scarring of blood vessel walls, which can restrict blood flow and cause damage to organs and tissues. Vasculitis can affect various types and sizes of blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries, and can impact different parts of the body.
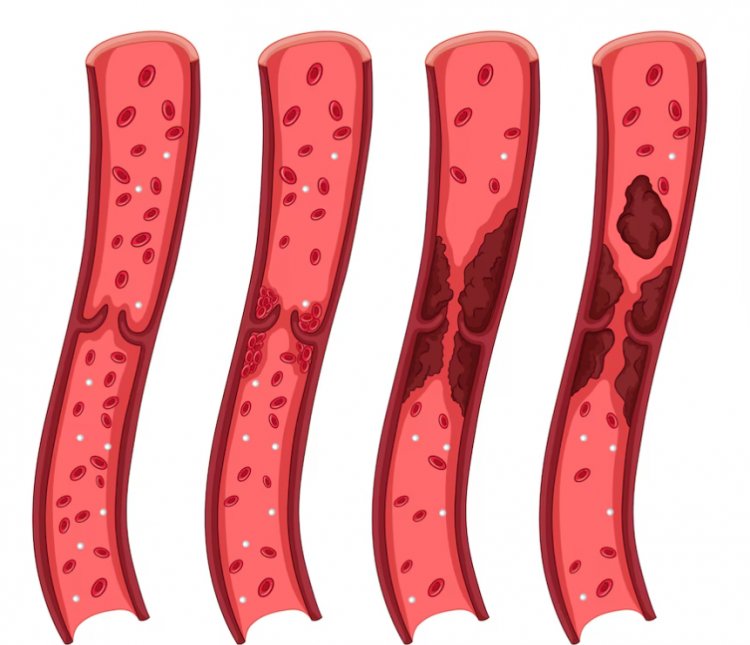
What Are the Symptoms of Vasculitis?
The symptoms of vasculitis vary widely depending on the type of blood vessels affected and the organs involved. General symptoms may include:
- Fever: Elevated body temperature due to inflammation.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and weakness.
- Muscle and Joint Pain: Pain in muscles and joints.
- Weight Loss: Unintended weight loss due to reduced appetite.
- Skin Rashes: Red spots, bruising, or rashes on the skin.
- Nerve Problems: Numbness, tingling, or weakness in limbs.
- Organ Dysfunction: Impaired function of vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, or lungs.
What Causes Vasculitis?
The exact causes of vasculitis are not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
- Autoimmune Diseases: The immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own blood vessels.
- Infections: Certain viral and bacterial infections can trigger vasculitis.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of vasculitis may increase the risk.
- Medications: Some drugs can cause vasculitis as a side effect.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals and smoking can contribute to the development of vasculitis.
Types of Vasculitis
Vasculitis is classified based on the size of the blood vessels affected. Major types include:
- Large Vessel Vasculitis: Includes conditions like Giant Cell Arteritis and Takayasu Arteritis, which affect large arteries.
- Medium Vessel Vasculitis: Includes diseases such as Kawasaki Disease and Polyarteritis Nodosa, which affect medium-sized arteries.
- Small Vessel Vasculitis: Includes conditions like Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis, Microscopic Polyangiitis, and Henoch-Schönlein Purpura, which affect small blood vessels.
How is Vasculitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing vasculitis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. The diagnostic process includes:
- Blood Tests: To detect inflammation, infection, and immune system abnormalities.
- Urine Tests: To assess kidney function and detect abnormalities.
- Imaging Studies: Techniques such as MRI, CT scans, and ultrasound are used to visualize blood vessels and affected organs.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample from the affected area is examined under a microscope to confirm inflammation and damage.
Treatment Methods for Vasculitis
The treatment of vasculitis depends on the specific type, severity, and organs involved. Common treatment methods include:
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly used to reduce inflammation.
- Immunosuppressive Medications: Drugs such as cyclophosphamide and methotrexate help control the immune system's overactivity.
- Biologic Agents: Medications like rituximab target specific components of the immune system and are used in severe cases.
- Supportive Therapies: Pain relievers, antihypertensive drugs, and treatments to support organ function may be necessary.
- Infection Treatment: Appropriate antibiotics or antiviral medications are used if an infection triggers vasculitis.
Vasculitis is a complex group of diseases that can affect various parts of the body due to blood vessel inflammation. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment are crucial for managing the disease and preventing organ damage. Continuous monitoring and individualized care plans help improve the quality of life for patients with vasculitis. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to manage the condition effectively and address any complications promptly.
Understanding the Impact of Vasculitis on Daily Life
Living with vasculitis can be challenging, and its impact on daily life varies depending on the severity and organs affected. Patients often need to adapt their lifestyles to manage symptoms and minimize complications. Key aspects include:
- Diet and Nutrition: A balanced diet can help maintain overall health and support the immune system. Patients may need to adjust their diet to manage weight loss or gain and accommodate medication side effects.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity is important for maintaining muscle strength and joint flexibility. However, exercise routines may need to be modified to avoid overexertion and accommodate fatigue.
- Stress Management: Chronic illness can be stressful, and finding ways to manage stress is crucial. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and counseling can be beneficial.
- Medication Adherence: Consistently taking prescribed medications is vital for controlling inflammation and preventing flare-ups. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to manage any side effects.
Research and Advances in Vasculitis Treatment
Ongoing research is critical to understanding vasculitis better and developing new treatments. Recent advances include:
- Biologic Therapies: New biologic agents that target specific pathways in the immune system are being studied and show promise in treating various types of vasculitis.
- Genetic Studies: Research into the genetic basis of vasculitis aims to identify risk factors and potential targets for therapy.
- Improved Diagnostic Tools: Advances in imaging technology and biomarkers are enhancing the ability to diagnose vasculitis earlier and more accurately.
Support and Resources for Vasculitis Patients
Support networks and resources are essential for individuals living with vasculitis. Organizations such as the Vasculitis Foundation provide valuable information, support groups, and advocacy for patients and their families. Connecting with others who understand the challenges of vasculitis can offer emotional support and practical advice.
Conclusion
Vasculitis is a multifaceted disease requiring a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, treatment, and management. Early detection and personalized treatment plans are essential for controlling the disease and improving patient outcomes. Ongoing research and advancements in medical science continue to provide hope for better treatments and ultimately a cure for vasculitis. By staying informed and actively participating in their care, patients with vasculitis can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by the disease.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
Hashtags:
#Vasculitis #Health #MedicalAdvice #AutoimmuneDisease #ChronicIllness #Inflammation #VascularHealth #PatientSupport #MedicalResearch #Healthcare
What's Your Reaction?





















