Beyond the Pins and Needles: Exploring the Depths of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition characterized by damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves, which are the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. These nerves are responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body, including the limbs, organs, and skin. When these nerves become damaged or impaired, it can lead to a wide range of symptoms and complications. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for peripheral neuropathy.
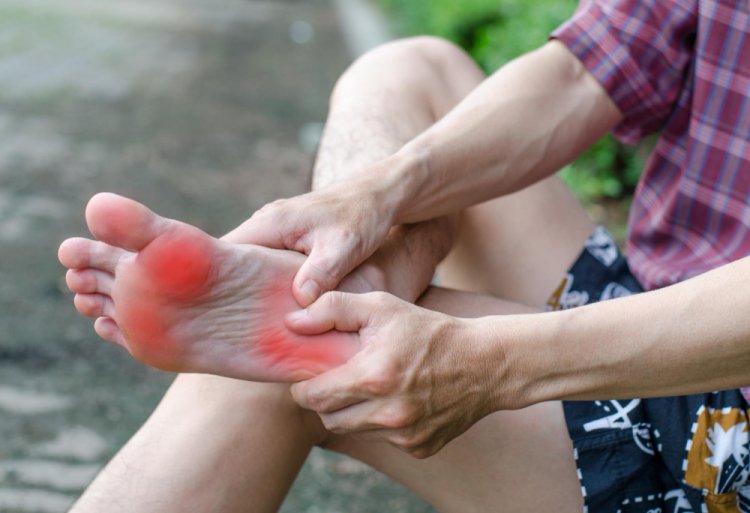
Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy:
Peripheral neuropathy can have various causes, including:
-
Diabetes: Diabetic neuropathy is one of the most common causes of peripheral neuropathy. Prolonged high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, particularly in the legs and feet.
-
Trauma: Physical injuries such as fractures, crush injuries, or compression injuries can directly damage the peripheral nerves, leading to neuropathy.
-
Infections: Certain infections can affect the peripheral nerves and cause neuropathy. These infections may include Lyme disease, HIV/AIDS, hepatitis C, and leprosy.
-
Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Guillain-Barré syndrome can trigger an immune response that attacks the peripheral nerves, resulting in neuropathy.
-
Toxins: Exposure to certain toxins, chemicals, or heavy metals can damage the peripheral nerves and lead to neuropathy. Examples include alcohol abuse, chemotherapy drugs, and industrial chemicals.
-
Medications: Some medications, particularly chemotherapy drugs, antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV/AIDS, and certain antibiotics, can cause peripheral neuropathy as a side effect.
-
Genetic Factors: Inherited disorders such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and hereditary neuropathies can cause peripheral neuropathy.
Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy:
The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy can vary widely depending on the type of nerves affected and the extent of the damage. Common symptoms include:
-
Tingling or numbness: Patients may experience a sensation of pins and needles, tingling, or numbness in the affected areas, often starting in the toes or fingers and spreading gradually.
-
Burning or shooting pain: Some individuals may experience sharp, stabbing pains or a constant burning sensation, which can be severe and debilitating.
-
Muscle weakness: Weakness or difficulty moving the affected limbs or muscles may occur, making it challenging to perform everyday tasks such as walking or grasping objects.
-
Sensitivity to touch: Even light touch or pressure on the skin can cause discomfort or pain, known as allodynia.
-
Loss of coordination: Peripheral neuropathy can affect balance and coordination, increasing the risk of falls and injuries.
-
Changes in skin, hair, or nails: Neuropathy can lead to changes in the texture, color, or temperature of the skin, as well as hair loss or abnormal nail growth in the affected areas.
Diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathy:
Diagnosing peripheral neuropathy typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, including:
-
Medical History: The doctor will review the patient's medical history, including any underlying conditions, medications, or recent injuries or illnesses.
-
Physical Examination: A thorough neurological examination may be performed to assess reflexes, muscle strength, sensation, and coordination.
-
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) and Electromyography (EMG): These tests measure the speed and strength of electrical signals traveling along the nerves, helping to identify nerve damage and determine its severity.
-
Blood Tests and Imaging Studies: These may be ordered to check for underlying conditions or structural abnormalities that may be contributing to neuropathy.
Treatment Options for Peripheral Neuropathy:
While peripheral neuropathy can be challenging to treat, several approaches may help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
-
Medications: Pain relievers such as over-the-counter analgesics or prescription medications may be prescribed to alleviate neuropathic pain.
-
Physical Therapy: Therapy can help improve strength, flexibility, balance, and coordination.
-
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): This therapy may help disrupt pain signals and provide temporary relief.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Making healthy lifestyle choices can help prevent further nerve damage and improve overall health.
-
Alternative Therapies: Some patients may find relief from complementary and alternative therapies.
-
Surgical Intervention: In cases where surgery is needed to relieve pressure on the nerves or repair damaged structures.
In conclusion, Peripheral neuropathy is a complex and often debilitating condition that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Early diagnosis, comprehensive evaluation, and personalized treatment are essential for effectively managing symptoms, preventing complications, and improving long-term outcomes for patients with neuropathy. If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of peripheral neuropathy, it is crucial to seek prompt medical attention from a qualified healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
#PeripheralNeuropathy #NeuropathyAwareness #NerveDamage #PainManagement #Neurology #Healthcare #ChronicPain #NeurologicalDisorders #HealthyLiving #MedicalTreatment #NeuroRehabilitation #WellnessJourney #NerveHealth #LifestyleChanges #PainReliefOptions #NeuropathySupport #HolisticHealth #PhysicalTherapy #NeurologyUpdates #HealthEducation
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
What's Your Reaction?





















