Behçet's Disease: An Overview
Behçet's disease, named after the Turkish dermatologist Hulusi Behçet who first described it in 1937, is a rare chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by inflammation of blood vessels throughout the body. It primarily affects multiple systems including the skin, mucous membranes, eyes, and joints. Behçet's disease is more prevalent in regions along the ancient Silk Road, including the Middle East, Mediterranean countries, and East Asia, although it can occur in any population.
Symptoms
Behçet's disease can manifest in various ways, and its symptoms may fluctuate over time. Some of the common signs and symptoms include:
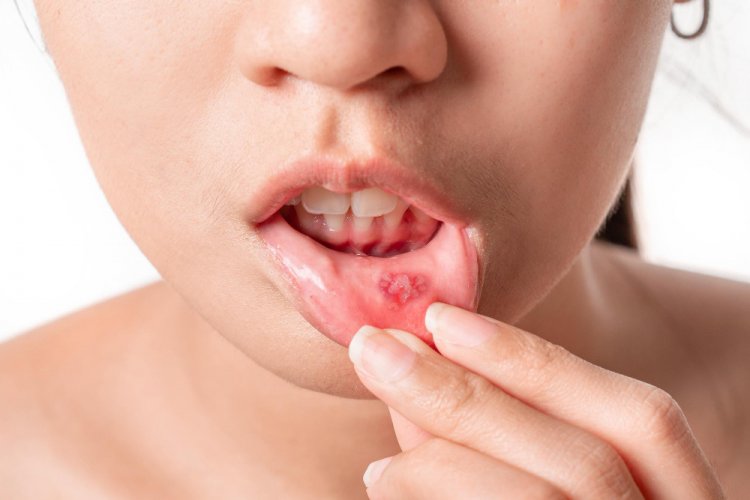
Recurrent Oral Ulcers
Painful mouth ulcers are often the initial symptom, appearing as round or oval sores that heal within 1 to 3 weeks.
Genital Ulcers
Similarly, painful ulcers may develop on the genitals, affecting both men and women. These ulcers can be large and may leave scars upon healing.
Skin Lesions
Skin lesions such as acne-like nodules, erythema nodosum (painful red nodules on the legs), and folliculitis (inflammation of hair follicles) may occur.
Eye Inflammation
Inflammation of the eyes (uveitis) can lead to redness, pain, blurred vision, and in severe cases, blindness if left untreated.
Joint Pain
Joint pain and swelling, resembling symptoms of arthritis, can affect the knees, ankles, wrists, and other joints.
Central Nervous System Involvement
In rare cases, Behçet's disease can affect the central nervous system, causing symptoms such as headache, confusion, seizures, and stroke-like symptoms.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Behçet's disease can be challenging due to its variable presentation and overlap with other conditions. There's no specific test for Behçet's disease, so diagnosis is typically based on a combination of clinical symptoms and exclusion of other possible causes. Diagnostic criteria often include the presence of recurrent oral ulcers along with other characteristic symptoms.
Treatment
The goals of treatment for Behçet's disease are to reduce inflammation, alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. Treatment may involve a combination of medications such as:
- Corticosteroids: These are often used to reduce inflammation during acute flare-ups.
- Immunosuppressants: Drugs like azathioprine, methotrexate, or cyclosporine may be prescribed to suppress the immune system and prevent recurrent episodes.
- Biologic Therapies: In cases of severe or refractory Behçet's disease, biologic agents such as TNF-alpha inhibitors (e.g., infliximab) may be considered.
Complications
If left untreated or inadequately managed, Behçet's disease can lead to serious complications including:
- Blindness: Untreated eye inflammation can cause irreversible damage to the retina and optic nerve, leading to blindness.
- Neurological Complications: Central nervous system involvement can result in strokes, seizures, and other neurological deficits.
- Vascular Complications: Inflammation of blood vessels can lead to blood clots, aneurysms, and other vascular problems.
- Gastrointestinal Complications: Severe inflammation in the digestive tract can cause abdominal pain, bleeding, and bowel perforation.
In conclusion, Behçet's disease is a complex condition with diverse manifestations that require a multidisciplinary approach to management. While there's currently no cure for Behçet's disease, prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help control symptoms, prevent complications, and improve the long-term outlook for affected individuals. Further research into the underlying mechanisms of the disease is needed to develop more targeted therapies and improve patient outcomes.
#BehcetsDisease #AutoimmuneDisorder #ChronicIllness #Inflammation #RareDisease #HealthAwareness #MedicalResearch #TreatmentOptions #SymptomManagement #PatientCare #DiseaseAwareness #HealthEducation #Immunosuppressants #Corticosteroids #BiologicTherapies #MedicalScience #EyeHealth #JointPain #NeurologicalComplications #VascularHealth #GastrointestinalHealth #QualityOfLife #HealthcareGoals
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
What's Your Reaction?





















