Asbestosis: A Silent Threat
Asbestosis stands as a grim testament to humanity's sometimes unwitting dance with industrial progress. This insidious lung condition, characterized by fibrosis and scarring, arises from prolonged exposure to asbestos fibers. While its onset may be subtle, the repercussions are profound, impacting individuals long after their initial contact with this hazardous mineral. This article endeavors to delve deeper into the multifaceted aspects of asbestosis, encompassing its origins, clinical manifestations, diagnostic modalities, therapeutic interventions, and preventive strategies. #Asbestosis #LungDisease #AsbestosExposure #OccupationalHazard #RespiratoryIllness #HealthAwareness #IndustrialHealth #WorkplaceSafety #PublicHealth #PreventiveHealthcare #HealthEducation #EnvironmentalHealth #OccupationalHealth #SafetyRegulations #HealthcareAwareness #HealthAndSafety #RespiratoryHealth #HealthyLiving #HealthEducation #HealthPromotion
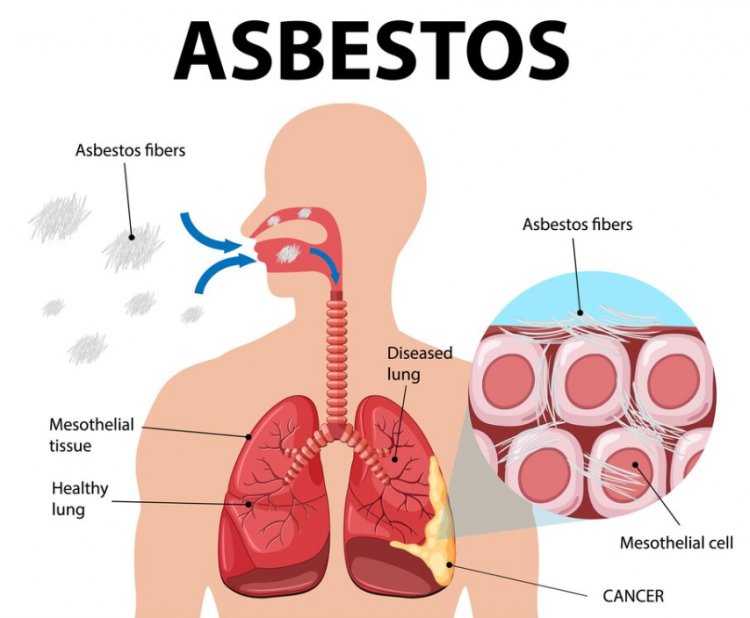
Origins and Epidemiology
Asbestos, hailed for its versatility and resilience, found widespread application across industries ranging from construction to shipbuilding throughout much of the 20th century. Its utilization peaked during periods of industrial expansion, with workers unwittingly inhaling its microscopic fibers as they toiled in factories, shipyards, and construction sites. Consequently, the prevalence of asbestosis surged, punctuating the landscape of occupational lung diseases with a silent but formidable presence. Even today, despite heightened awareness and regulatory measures, the legacy of past asbestos use continues to reverberate, with new cases emerging among those exposed decades ago.
Pathophysiology
At the heart of asbestosis lies a complex interplay of cellular and molecular events triggered by the inhalation of asbestos fibers. These fibers, once airborne, infiltrate the respiratory tract, where they may persist for years, if not decades. Within the lungs, they provoke a cascade of inflammatory responses, culminating in the deposition of collagen and fibrous tissue. Over time, this relentless fibrotic process impairs lung function, diminishes respiratory capacity, and compromises gas exchange, laying the groundwork for the clinical sequelae of asbestosis.
Clinical Manifestations
The clinical presentation of asbestosis is often insidious, unfolding over a protracted period marked by latency periods that extend beyond 20 or 30 years. Initial symptoms, such as dyspnea on exertion and a dry, persistent cough, may be dismissed as benign or attributed to other causes. However, as the disease progresses, these symptoms intensify, accompanied by chest tightness, wheezing, and an insidious decline in exercise tolerance. In advanced stages, asbestosis may precipitate respiratory failure, cor pulmonale, and an increased susceptibility to respiratory infections, casting a pall over the afflicted individual's quality of life.
Diagnostic Modalities
Accurate diagnosis of asbestosis hinges on a multifaceted approach that integrates clinical evaluation, radiological imaging, and pulmonary function testing. Chest radiographs may reveal characteristic findings, including reticular opacities, pleural plaques, and diaphragmatic thickening. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) offers enhanced sensitivity in detecting subtle parenchymal changes, such as honeycombing and traction bronchiectasis. Pulmonary function tests, encompassing spirometry and diffusion capacity measurements, provide valuable insights into lung mechanics and the extent of impairment attributable to asbestosis.
Therapeutic Interventions
Regrettably, asbestosis defies curative intervention, necessitating a therapeutic paradigm focused on symptom management and supportive care. Pharmacological agents, such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids, may afford symptomatic relief and mitigate inflammation, albeit with limited efficacy. Supplemental oxygen therapy, administered via nasal cannula or face mask, serves to ameliorate hypoxemia and improve exercise tolerance, thereby enhancing the patient's functional capacity and quality of life. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs, comprising exercise training, education, and psychosocial support, represent a cornerstone of holistic care, empowering individuals to cope with the physical and emotional challenges posed by asbestosis.
Preventive Strategies
Preventing asbestosis necessitates a concerted effort encompassing legislative measures, occupational health initiatives, and public awareness campaigns. Regulatory frameworks, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards, mandate stringent controls on asbestos exposure in occupational settings, stipulating permissible exposure limits and delineating engineering controls for hazard mitigation. Comprehensive risk assessments, periodic surveillance, and medical monitoring programs are indispensable components of occupational health surveillance, facilitating early detection of asbestos-related diseases and prompt implementation of preventive measures. Furthermore, public education initiatives aimed at homeowners, contractors, and renovation professionals underscore the importance of asbestos awareness, advocating for safe handling practices during building renovations and demolitions to minimize environmental contamination and safeguard public health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, asbestosis epitomizes the enduring legacy of industrialization, underscoring the profound consequences of human interaction with hazardous materials. While progress has been made in curtailing asbestos exposure and mitigating its deleterious effects, the specter of asbestosis persists, serving as a stark reminder of the collective responsibility to safeguard occupational and environmental health. Through continued vigilance, rigorous enforcement of regulatory safeguards, and concerted efforts to raise awareness, we can aspire to mitigate the burden of asbestosis and foster a safer, healthier future for generations to come.
Discover Coupoly's exclusive Medical Concierge Service, connecting you with renowned doctors and clinics, whether in the UK or abroad.
Get in Touch
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
What's Your Reaction?





















