A Comprehensive Guide to Hysterectomy: Procedures, Risks, and Recovery
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the uterus (womb). This surgery is performed for various medical reasons, including
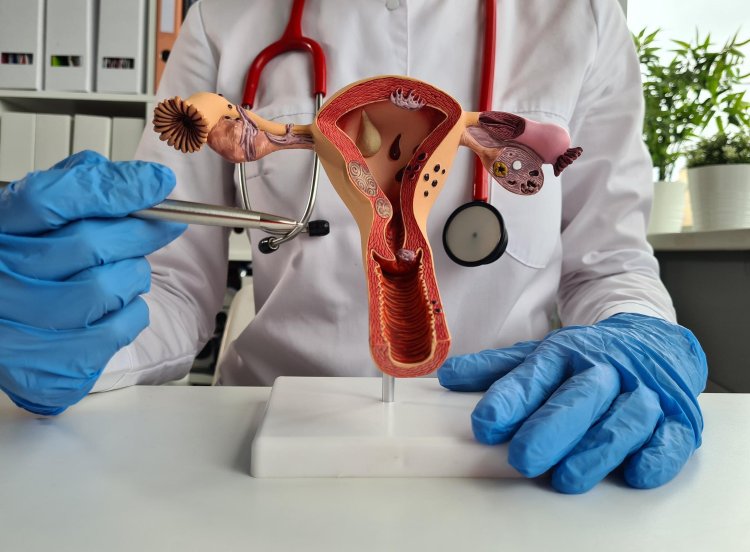
Uterine Fibroids
Non-cancerous growths in the uterus causing pain, bleeding, or other complications.
Endometriosis
A condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus grows outside it, causing pain and infertility.
Chronic Pelvic Pain
Persistent pain in the pelvic region.
Uterine Prolapse
When the uterus descends into or outside the vaginal canal.
Cancer
Cancers of the uterus, cervix, or ovaries.
Types of Hysterectomies
There are several types of hysterectomies, each defined by the extent of tissue removal:
Total Hysterectomy
Removal of the entire uterus, including the cervix.
Subtotal or Partial Hysterectomy
Removal of the upper part of the uterus, leaving the cervix intact.
Radical Hysterectomy
Removal of the uterus, cervix, part of the vagina, and surrounding tissues, typically performed when cancer is present.
How is a Hysterectomy Performed?
Hysterectomies can be performed using different surgical approaches, tailored to the patient's condition, the reason for surgery, and the surgeon’s expertise. The primary techniques are:
Abdominal Hysterectomy
- Procedure: A larger incision is made in the lower abdomen.
- Advantages: Provides the surgeon with a clear view of the pelvic organs.
- Uses: Often used for larger uteri or when malignancy is suspected.
- Recovery: Longer recovery time due to the larger incision.
Vaginal Hysterectomy
- Procedure: The uterus is removed through an incision in the vagina.
- Advantages: No external scars and usually a quicker recovery.
- Uses: Suitable for uterine prolapse or other non-cancerous conditions.
- Recovery: Generally shorter recovery time compared to abdominal surgery.
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
- Procedure: Small incisions are made in the abdomen for inserting a camera and surgical instruments.
- Advantages: Minimally invasive, leading to quicker recovery and less postoperative pain.
- Uses: Can be used for a variety of conditions and often combined with vaginal hysterectomy (LAVH).
- Recovery: Shorter recovery time and less postoperative discomfort.
Robotic-Assisted Hysterectomy
- Procedure: Similar to laparoscopic surgery but with robotic instruments controlled by the surgeon.
- Advantages: Enhanced precision, beneficial for complex cases.
- Uses: Ideal for intricate surgeries requiring delicate manipulation.
- Recovery: Similar to laparoscopic surgery with minimal downtime.
Hysterectomy in Older Women
Older women undergoing hysterectomy may face different considerations compared to younger patients. These include:
- Comorbidities: Conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and other age-related health issues.
- Bone Density: Increased risk of osteoporosis if the ovaries are removed.
- Hormonal Changes: Potential for more pronounced symptoms if menopause is induced by surgery.
- Recovery: May take longer due to overall physical health.
Preoperative assessment is crucial for older women to minimize risks and ensure a tailored surgical approach.
Risks Associated with Hysterectomy
While a hysterectomy is generally safe, it carries potential risks, such as:
- Infection: Risk of postoperative infections.
- Bleeding: Significant blood loss during or after surgery.
- Injury to Surrounding Organs: Such as the bladder, intestines, or blood vessels.
- Anesthesia Complications: Possible adverse reactions to anesthesia.
- Long-term Effects: Including hormonal changes, especially if the ovaries are removed, leading to early menopause and associated symptoms.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
Postoperative care is critical for a smooth recovery. General guidelines include:
- Rest: Adequate rest is essential for healing.
- Avoiding Strenuous Activities: Refrain from heavy lifting and vigorous exercise for at least six weeks.
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular check-ups with the healthcare provider to monitor healing and address any complications.
- Managing Pain: Use of prescribed pain relief medications as needed.
- Healthy Diet and Hydration: Ensuring proper nutrition and hydration to support recovery.
Recovery Time
The recovery period varies based on the type of hysterectomy and individual health:
- Abdominal Hysterectomy: Typically, 6 to 8 weeks for full recovery.
- Vaginal or Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Generally, 3 to 4 weeks for full recovery.
- Robotic-Assisted Hysterectomy: Recovery time is similar to laparoscopic surgery, often within 3 to 4 weeks.
Conclusion
A hysterectomy can significantly improve the quality of life for women suffering from severe uterine conditions. Understanding the procedure, associated risks, and postoperative care is crucial for achieving the best possible outcomes. Patients should consult with their healthcare providers to determine the most suitable approach based on their individual health needs and circumstances.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have any health concerns or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or clinic, for proper diagnosis and treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
#UterineFibroids #Endometriosis #ChronicPelvicPain #UterineProlapse #Cancer #Hysterectomy #WomensHealth #Surgery #MedicalCare #Recovery #Healthcare
What's Your Reaction?





















